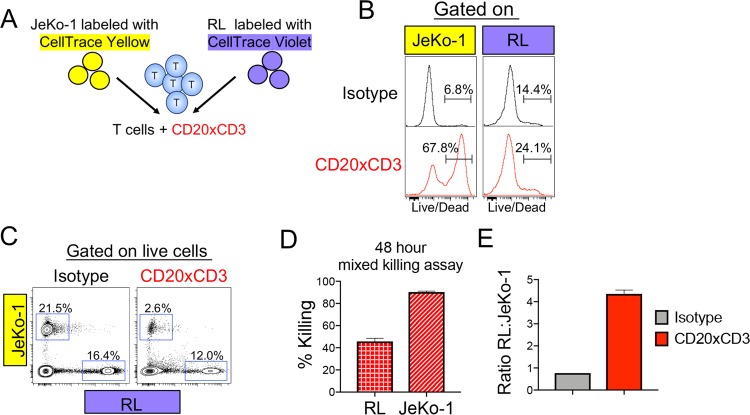
Figure 2.
Tumor cell-intrinsic factors mediate differential sensitivity to CD20xCD3-induced T cell killing. (A) JeKo-1 tumor cells were labeled with CellTrace Yellow (CTY), and RL tumor cells were labeled with CellTrace Violet (CTV). Labeled tumor cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and co-cultured with healthy donor T cells (3:1 E:T) and 30 ng/ml CD20xCD3 bsAb or CD3-binding isotype control antibody for 48 hours, followed by staining with viability dye and FACS analysis. (B) Representative histograms show viability staining of JeKo-1 (CTY+) and RL (CTV+) cells after co-culture with T cells and CD20xCD3 bsAb or CD3-binding isotype control antibody. (C) Representative FACS plots show relative proportions of live JeKo-1 and RL tumor cells in co-culture with T cells and CD20xCD3 bsAb or CD3-binding isotype control antibody. (D) The percent killing for JeKo-1 and RL tumor cells in a mixed killing assay was calculated by quantifying the number of live cells remaining after CD20xCD3 bsAb treatment compared to CD3-binding isotype control antibody. (E) Decreased sensitivity of RL cells to T cell-mediated killing results in an increase in the ratio of live RL tumor cells to live JeKo-1 tumor cells after 48 hours of CD20xCD3 bsAb treatment.