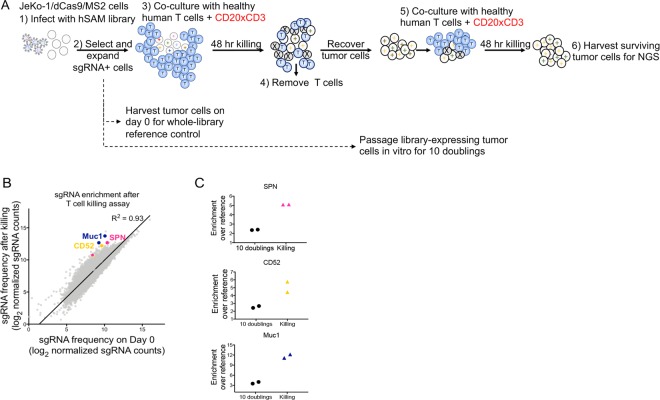
Figure 3.
Genome-scale CRISPR transcriptional activation screen in Jeko-1 cells. (A) JeKo-1/dCas9/MS2 cells were infected with a human CRISPR SAM library of 70,290 sgRNAs. sgRNA-expressing cells were co-cultured with human T cells (3:1) E:T and 30 ng/ml CD20xCD3 bsAb. Triplicate killing assays were set up at 500x library representation. After an initial killing assay of 48 hours, T cells were removed by anti- CD3 positive selection, surviving tumor cells were expanded, and the killing assay was repeated with fresh T cells and CD20xCD3 bsAb. After 48 hours, surviving tumor cells were harvested and processed for Next-Generation Sequencing and comparison of sgRNA representation to that in reference control tumor cells harvested immediately after antibiotic selection. In parallel with T cell killing assays, library-modified JeKo-1/dCas9/MS2 cells were passaged in vitro and harvested after 10 doublings. (B) Comparison of normalized sgRNA counts in the tumor cell population collected after T cell killing compared to tumor cells harvested on day 0 before T cell killing. Normalized sgRNA counts were averaged across triplicate samples for each condition. 3 genes of interest (SPN, CD52, and MUC1), each with 2 top-scoring sgRNAs are highlighted. R2 value calculated by Pearson’s correlation. (C) Enrichment of 2 sgRNAs targeting SPN, CD52, or MUC1 in tumor cells passaged in vitro for 10 doublings and in tumor cells that survived CD20xCD3-mediated T cell killing.