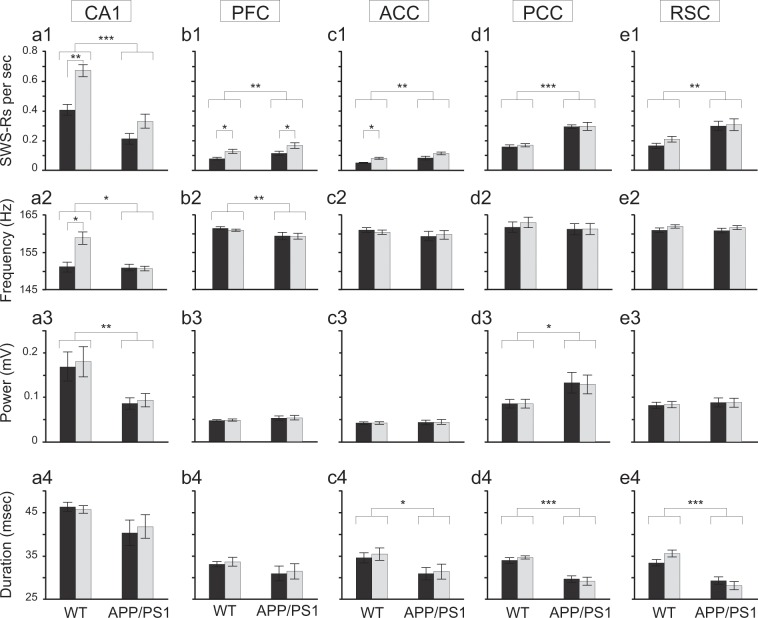
Figure 3.
Impairment of hippocampal ripples and enhanced expression of cortical ripples during SWS in APP-PS1 mice. (a1-4). CA1 ripples in APP-PS1 group expressed lower occurrence rate (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 17.23, P = 0.000, Friedman’s test), frequency (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 4.39, P = 0.038, Friedman’s test) and power (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 7.35, P = 0.007, Friedman’s test) than controls whereas ripple duration remained similar in both groups (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 1.84, P = 0.17, Friedman’s test). Post-learning increase of ripple occurrence rate (WT: N = 7, P = 0.005, Wilcoxon rank-sum; APP/PS1: N = 7, P = 0.106, Wilcoxon rank-sum) and oscillation frequency (WT: N = 7, P = 0.014, Wilcoxon rank-sum; APP/PS1: N = 7, P = 0.91, Wilcoxon rank-sum) was significant only in control animals. (b1-4,c1-4). Cortical ripple occurrence rate was significantly higher in APP/PS1 than control mice in PFC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 6.86, P = 0.009, Friedman’s test) and ACC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 9,44, P = 0.002, Friedman’s test). Post-learning increase of ripple occurrence was expressed in controls, both in PFC (N = 7, P = 0.011, Wilcoxon rank-sum) and ACC (N = 7, P = 0.002, Wilcoxon rank-sum) as well as in APP/PS1 animals in PFC (N = 7, P = 0.038, Wilcoxon rank-sum). APP/PS1 mice expressed lower ripple frequency in PFC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 6.86, P = 0.009, Friedman’s test) and shorter ripple duration in ACC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 5.10, P = 0.024, Friedman’s test). No significant differences between groups were found in ripple frequency in ACC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 0.008, P = 0.93, Friedman’s test), ripple power in ACC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 0.008, P = 0.93, Friedman’s test) and PFC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 1.38, P = 0.24, Friedman’s test) and ripple duration in PFC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 1.6, P = 0.206, Friedman’s test). (d1-4,e1-4). Cortical ripples occurred more frequently in APP/PS1 animals, both in PCC (APP/PS1: N = 6, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 16.61, P = 0.000, Friedman’s test) and RSC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 10.58, P = 0.001, Freedman test). PCC ripples were expressed with a higher power in APP/PS1 group (APP/PS1: N = 6, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 5.12, P = 0.023, Friedman’s test). However, duration of cortical ripples was shorter in APP/PS1 animals both in PCC (APP/PS1: N = 6, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 15.70, P = 0.000, Friedman’s test) and RSC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 16.53, P = 0.000, Friedman’s test). No significant differences between groups were found in oscillation frequency in PCC (APP/PS1: N = 6, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 0.11, P = 0.73, Friedman’s test) and RSC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 0.13, P = 0.72, Friedman’s test), as well as in ripple power in RSC (APP/PS1: N = 7, WT: N = 7, chi-sq = 0.20, P = 0.65, Friedman’s test). No learning-dependent changes were found in PCC and RSC ripple properties. All box plot represent mean values before (dark) and after (light) learning, vertical bars represent standard errors.