Figure 4.
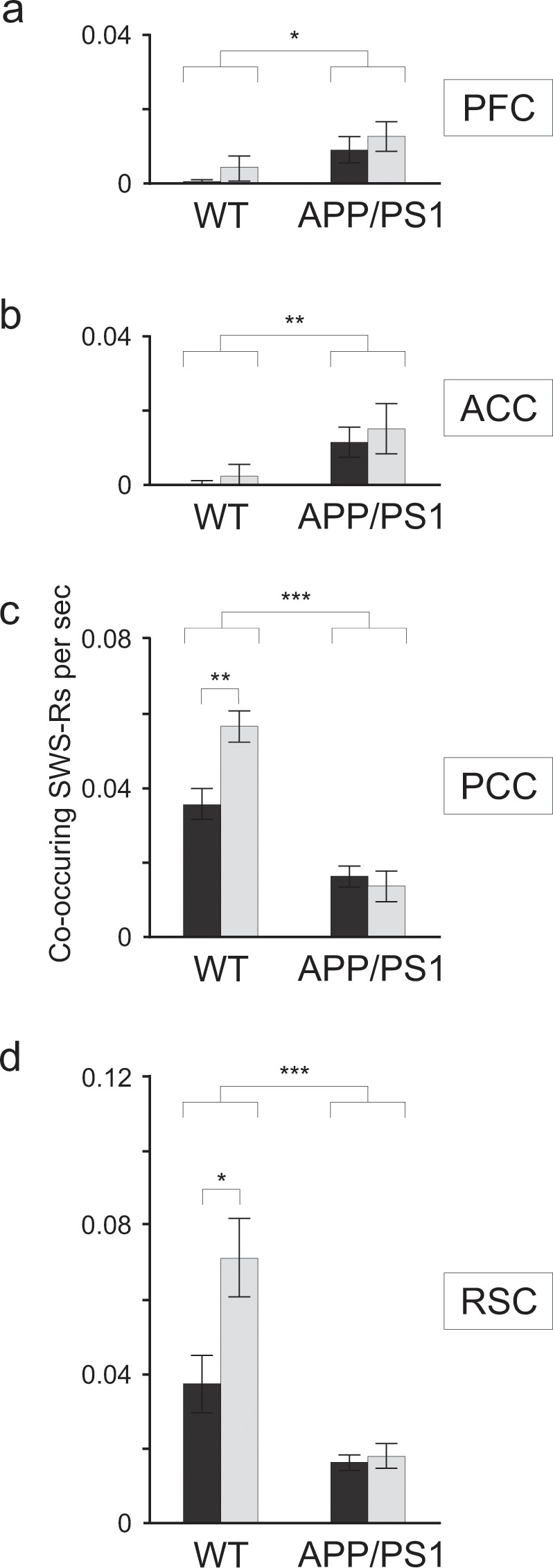
Co-occurrence of cortical and hippocampal ripples was altered in APP-PS1 mice. (a,b) In the control animals the rate of PCF and ACC ripples co-occurring with hippocampal ripples was not different from zero (P > 0.2, Wilcoxon signed rank), whereas in APP-PS1 animals the rate was significantly higher (ACC: N = 7, P = 0.004, Friedman’s test, PFC: N = 7, P = 0.011, Friedman’s test) but not learning dependent (P > 0.5, Wilcoxon rank-sum) c,d. In the WT group, the rate of PCC and RSC ripples co-occurring with CA1 ripples was significantly higher than in the APP-PS1 animals (N = 7, chi-sq = 13.13, P = 0.003, Friedman’s test (PCC); N = 7, chi-sq = 11.79, P = 0.001, Friedman’s test (RSC)). Moreover and in contrast to the APP-PS1 group the rate increased after learning (WT: N = 7, P = 0.008, Wilcoxon rank-sum; APP/PS1: N = 7, P = 0.93, Wilcoxon rank-sum (PCC); WT: N = 7, P = 0.026, Wilcoxon rank-sum; APP/PS1: N = 6, P = 0.804, Wilcoxon rank-sum (RSC)).
