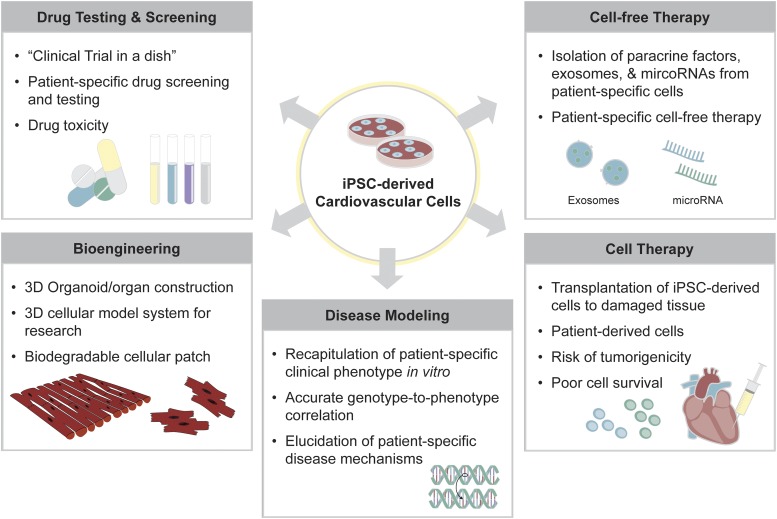
Fig. 1.
Applications of human iPSCs for precision medicine. Human iPSCs are differentiated to functional cardiovascular cells, providing an effective platform for patient-specific disease modeling, cell-based therapy, cell-free therapy, drug testing and screening, and bioengineered tissue construction. First, iPSC-derived cardiovascular cells can recapitulate patient-specific clinical phenotype in vitro, resulting in accurate genotype-to-phenotype correlation. iPSC-derived cells allow elucidation of patient-specific disease mechanisms, enabling drug screening and toxicity testing that are unique to the individual’s genetic and epigenetic makeup. iPSC-derived cells are also a source of cell-based therapy, allowing a patient’s own cells to be transplanted to the damaged tissue. In addition, exosomes and microRNAs secreted from patient-specific iPSC-derived cells allow them to be used for cell-free therapeutic purposes. Lastly, iPSC-derived cardiovascular cells can be engineered to create three-dimensional organoids or organ-like mimics of the heart or the blood vessels for advanced disease modeling. Overall, the risk of tumorigenicity and poor cell survival rate remain as challenges to be addressed.