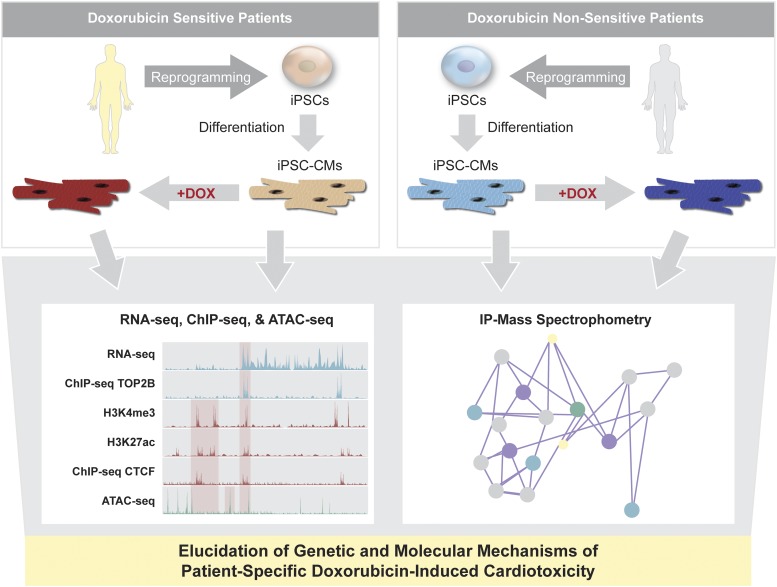
Fig. 5.
Elucidating mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Doxorubicin has shown cardiotoxicity for some patients. The patient-specific disease mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity remain poorly understood, and the direct and indirect effects of doxorubicin on CMs have not been clarified. Previous studies demonstrated that susceptibility of TOP2B to its target genes is dynamically modulated by doxorubicin. Using iPSC-derived CMs from doxorubicin-sensitive and nonsensitive patients, the transcriptional machinery of TOP2B can be determined by combining chromatin immunoprecipitation-seq, RNA-seq, transposase-accessible chromatin-seq, and immunoprecipitation–mass spectrometry. Cross-analysis of RNA-seq and chromatin immunoprecipitation-seq will further allow identification of direct target genes of TOP2B, which can be confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation-seq of TOP2B in human heart tissue. Verification of cardiac-specific target genes of TOP2B will lead to effective patient-specific therapeutics to combat doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.