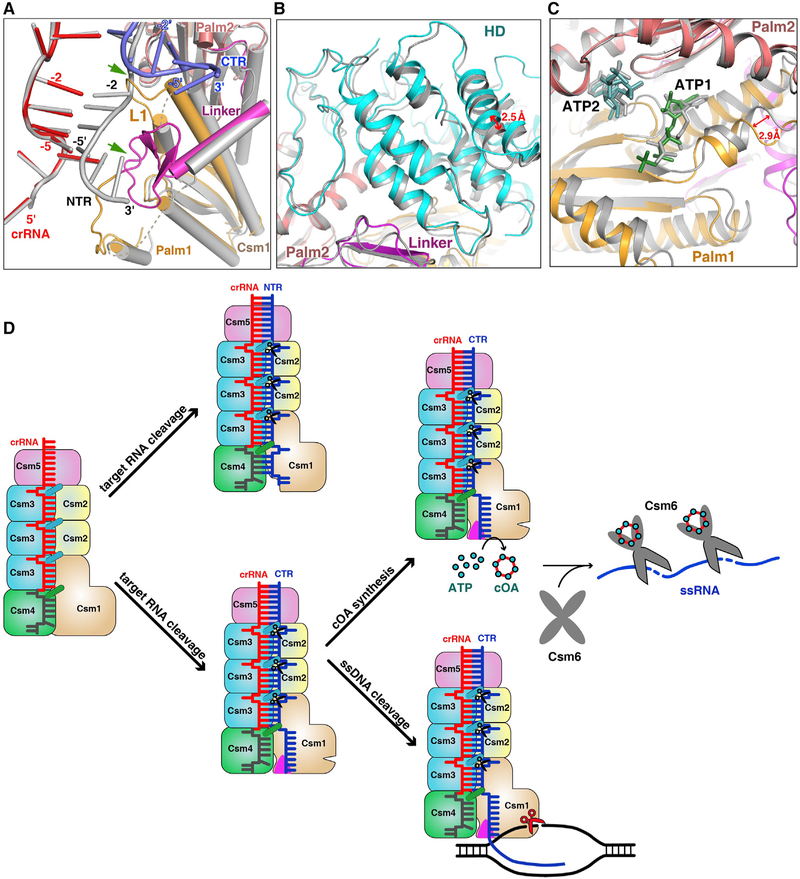
Figure 7. Non-complementarity of 3′ Anti-tag of Target RNA Activates the DNase and cOA Synthetase Activities.
(A) Structural comparison between NTR- and CTR-bound Csm complexes. Superposition of the NTR- and CTR-bound Csm complexes at the repeat region. The 5′ tag and 3′ anti-tag in the CTR-bound Csm complex are shown in red and blue, respectively. The Color-coding of Csm1 in the CTR-bound complex is identical to that used in Figure 1C. All components in the NTR-bound complex are shown in gray. Two green arrows highlight the clash region of between NTR and Csm1 within CTR-bound complex.
(B) Structural comparison of HD domains in the CTR- (cyan and purple) and NTR-bound (gray) Csm complexes by aligning the palm2 and D4 domains of the Csm1 subunit.
(C) Structural comparison of Palm domains in the CTR- (orange and salmon) and NTR- (gray) bound Csm complexes by aligning the palm2 and D4 domains of the Csm1 subunit.
(D) Model of type III-A interference. The crRNA associated with the Csm complex recognizes target RNA containing its complementary sequence forming the crRNA-target RNA duplex. The Csm3 subunit is an RNase that cleaves target RNA at 6-nt intervals. The 3′ anti-tag region of cognate target RNA binds to the Csm1 Linker and Loop L1 regions (shown in magenta triangles) and induces the rearrangement at the Linker and Loop L1 regions. This rearrangement of Csm1 allosterically activates the DNA cleavage and the production of cOAs, which activates the RNase activity of Csm6.
See also Figure S7.