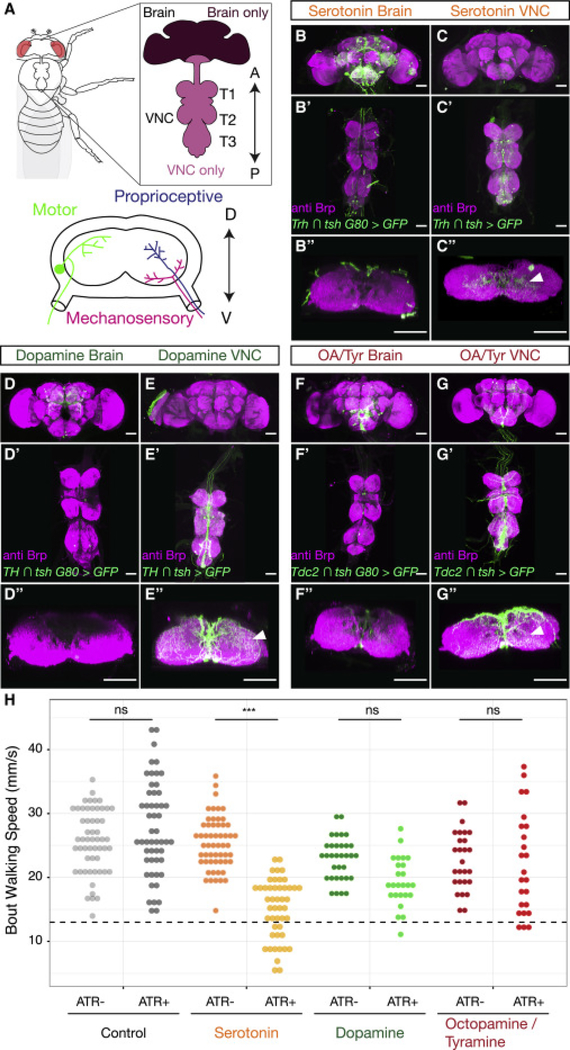
Figure 1. Neuromodulators in the Drosophila CNS.
A. The adult Drosophila CNS is composed of the brain and the VNC, which consists of three pairs of thoracic neuropils (T1, T2 and T3), each of which corresponds to a pair of adult legs, and an abdominal ganglion. The anterior (A)-posterior (P) axis is specified. Lower panel: Cross section of a thoracic neuropil illustrating projections of locomotor circuit components, including motor neurons, and sensory neurons that convey mechanosensory and proprioceptive information from the legs. The dorsal (D)– ventral (V) axis is specified.
B-G. Maximum intensity projections show the expression patterns driven by Gal4 lines labeling either brain-derived (B, D, F, Gal4 intersected with tsh Gal80) or VNC-derived (C, E, G, Gal4 intersected with tsh) serotonergic (B-C, Trh Gal4), dopaminergic (D-E, TH Gal4), or octopaminergic/tyraminergic (OA/Tyr) (F-G, Tdc2 Gal4) neurons. (B”-G”) Projection of a subset of cross sections of the VNC shows innervation of the T1 neuropil. Arrowheads point to innervation in the leg neuropils. All scale bars are 50 μm.
H. Optogenetic activation of serotonergic (Trh ∩ tsh > csChrimson) neurons in the Drosophila VNC, but not dopaminergic (TH ∩ tsh > csChrimson) or octopaminergic/tyraminergic (Tdc2 ∩ tsh > csChrimson) neurons, slows walking speed compared to all-trans-retinal (ATR) negative and non-Gal4 (w1118 ∩ tsh > csChrimson) controls. These experiments were carried out using the Flywalker assay (Mendes et al., 2013; see Figure S3 A for a schematic). * p<.05 **p<.01 ***p<.001 by Kruskal-wallis test with Dunn-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons. N walking bouts (animals) w1118 ATR− 55 (14–31); w1118 ATR+ 52 (14–36); Trh ATR− 56 (12–30); Trh ATR+ 47 (10–23); TH ATR− 33 (10–24); TH ATR+ 25 (10–26); Tdc2 ATR− 27 (10–27); Tdc2 ATR+ 24 (10–25).
See also Figure S1.