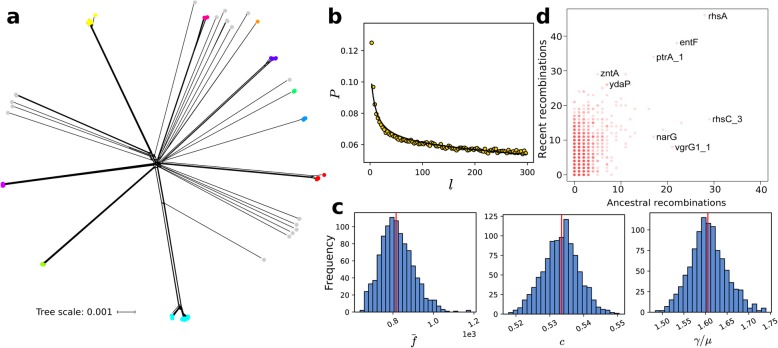
Fig. 3.
Recombination in C. sakazakii. (a) A phylogenetic network of the core genome generated using SplitsTree. Scale bar represents nucleotide substitutions per site. Colored dots represent BAPS clusters and are identical to those in Fig. 1a. (b) Correlation profile (circles) calculated from the core genomic alignment by mcorr. Model fit is shown as a solid line. (c) Frequency histograms showing the distributions of the three recombination parameters for all pairs of genomes. The red vertical lines indicate the means. (d) Genes that have undergone recent or ancestral recombination. Horizontal axis shows the estimated number of ancestral recombinations, and vertical axis shows the estimated number of recent recombinations. For visual clarity, names of some of the genes with known function are shown