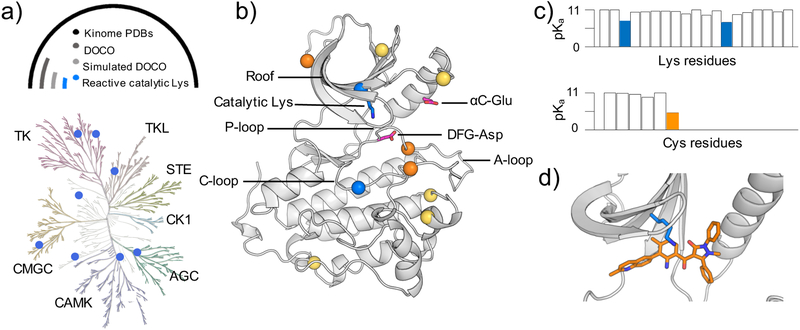
Figure 1. Identification of reactive lysines (and cysteines) in the human kinome.
a) Kinome tree representation of kinases (generated with KinMap16). The kinase groups are labeled; blue dots represent the kinases with predicted reactive lysines. Above the kinome tree, approximate proportions are given: unique PDB entries for the human kinome (4193), kinase genes with DOCO structures (306), DOCO structures, in which the catalytic lysine is not involved in any salt bridge (16), and structures with identified reactive catalytic lysine (8). Table 1 also contains a mutant EGFR and a c-SRC as validation cases. The complete list of kinases studied by CpHMD is given in Table S1. b) Retro- and prospectively predicted locations of reactive lysines (blue) and cysteines (orange: targeted in existing covalent inhibitors; yellow: prospectively predicted in this work) mapped on the EGFR structure (PDB: 5U8L). The catalytic lysine, αC-Glu, and DFG-Asp are shown in the stick model. c) Predicted lysine and cysteine pKa’s of PEK (PDB: 4X7N). d) A zoomed-in view shows the proximity of the type II reversible inhibitor (orange) and the catalytic lysine (blue) in PEK.