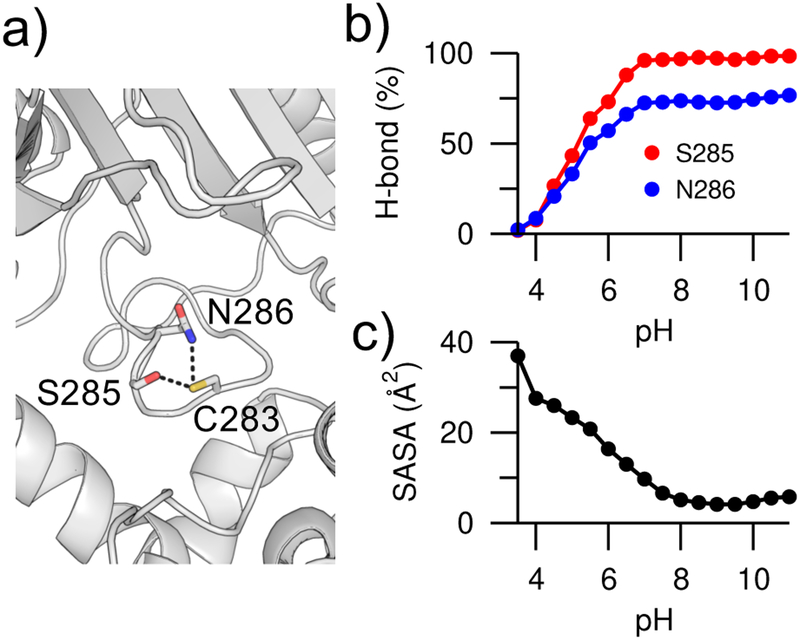
Figure 3. pH-dependent hydrogen bonding and solvent exposure.
a) Zoomed-in view of the hydrogen bonds between Cys283 and Ser285/Asn286 in creatine kinase (PDB: 1I0E). The hydroxyl of Ser285 and amide of Asn286 are the hydrogen bond donors, while the thiol of Cys283 is the hydrogen bond acceptor. b) Occupancies of the Cys283…Ser285 (red) and Cys283…Asn286 (blue) hydrogen bonds at different pH. To dene hydrogen bonds, a donor-acceptor heavy-atom distance of 3.5 Å and an angle of 30° were used. c) Solvent accessible surface area (SASA) of Lys74 in V74K SNase at different pH.