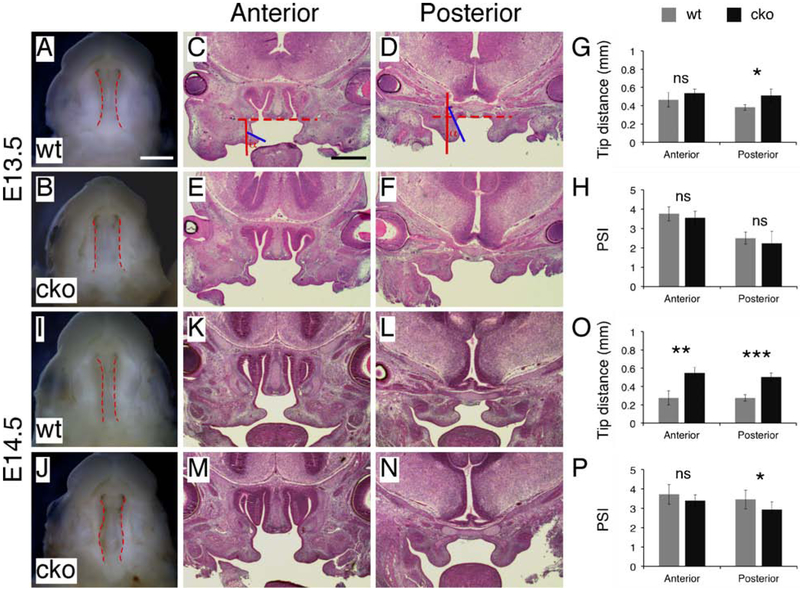
Figure 6.
Analysis of palatal shelf movement following ex vivo removal of the tongue and mandible. (A and B) Inferior view of the gap between the palatal shelves following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement in E13.5 wild type (A) and Has2 cko (B) embryos. Dashed red lines demarcating the medial edges of the palatal shelves. (C-F) Histological examination of palatal shelf morphology following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement in E13.5 wild type (C and D) and Has2 cko (E and F) embryos. The dashed and solid red lines in C and D marking the horizontal and vertical positions in the common oral-nasal cavity respectively. The angle (α) between the solid red and blue line used for calculating the PSI. (G) Measurements of the distance between the tips of the palatal shelves following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement in E13.5 wild type and Has2 cko embryos. (H) PSI in E13.5 wild type and Has2 cko embryos following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement. (I and J) Inferior view of the gap between the palatal shelves following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement in early E14.5 wild type (I) and Has2 cko (J) embryos. Dashed red lines demarcating the medial edges of the palatal shelves. (K-N) Histological examination of palatal shelf morphology following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement in early E14.5 wild type (K and L) and Has2 cko (M and N) embryos. (O) Measurements of the distance between the tips of the palatal shelves following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement in early E14.5 wild type and Has2 cko embryos. (P) PSI in early E14.5 wild type and Has2 cko embryos following ex vivo induction of palatal shelf movement. *, P value<0.05; **, P value<0.01; ***, P value<0.001; ns, not significant. Scale bar in A: 1mm; in C: 500μm.