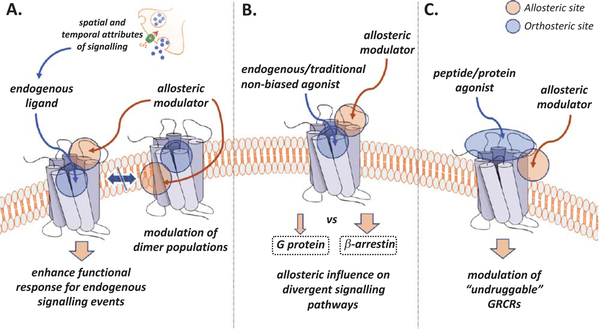
Fig. 2.
Applications of GPCR allosteric modulators and theoretical functional outcomes. A. Spatial and temporal signalling control is exemplified by neuronal neurotransmitter release. Allosteric modulation of functional response is only achieved for receptors bound to the neurotransmitter. Additionally, allosteric modulators may be used to alter GPCR dimer populations and consequential signalling patterns. B. GPCR structural conformations are critical drivers for biased signalling. Allosteric modulators may stabilize, disrupt, or induce structural conformations that preferentially (biased) signal via one or multiple pathways, at magnitudes unlike the endogenous ligand. C. Many GPCRs are targeted by large endogenous ligands, such as peptides and proteins. Small molecules may not sufficiently interact with the orthosteric site to induce signalling. Allosteric sites may offer promising, novel druggable surfaces.