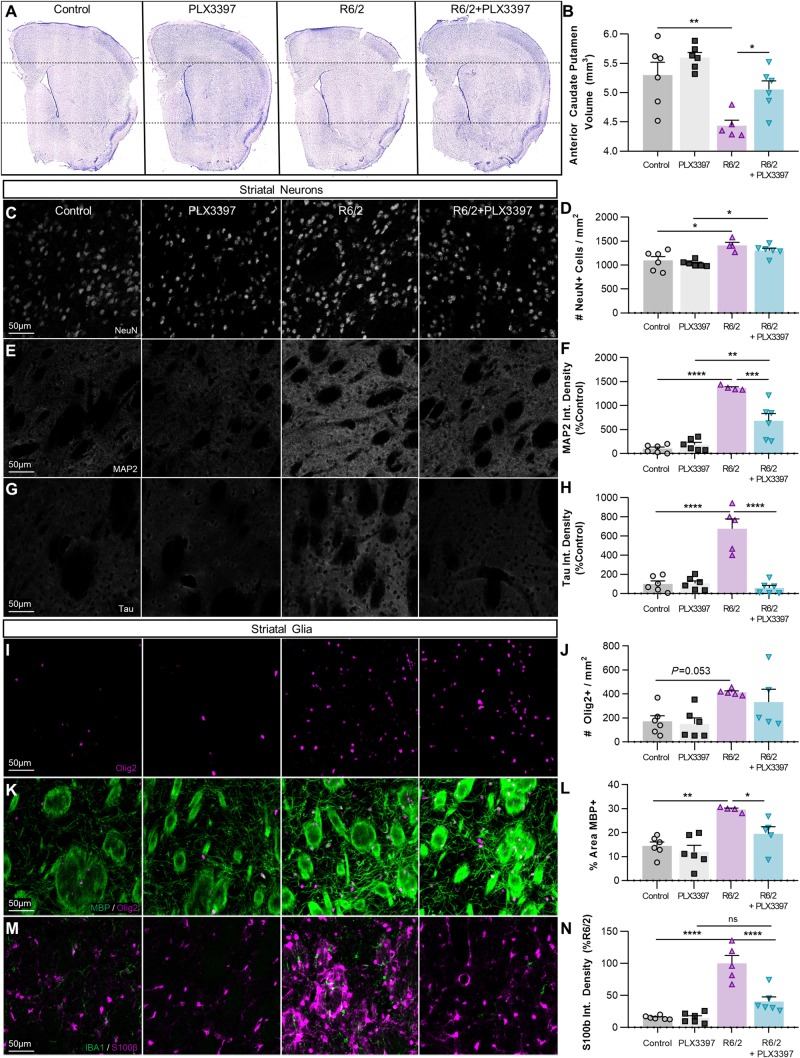
Figure 5.
PLX3397 prevents R6/2 striatal volume loss, neurite abnormalities, and astrogliosis. (A) Representative images of cresyl-violet stained coronal sections used for stereological assessment of striatal volume (n = 5–6/group, six sections/mouse separated by 240-μm intervals, spanning the anterior caudoputamen). (B) Quantification of stereological analysis reveals a significant reduction in R6/2 striatal volume versus control (P < 0.01) that is prevented with PLX3397 (P < 0.01) (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 5–6/group). (C–H) Investigation of striatal neurons revealed increased NeuN+ density (×20; C and D) in R6/2 and R6/2+PLX3397 mice compared to respective controls (P < 0.05) (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 4–6/group). Integrated MAP2+ (×20; E and F) and tau+ (×20; G and H) signal density, staining for microtubule-associated proteins localized to the dendrites and axons respectively, were significantly increased in R6/2 striatum versus control (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001) and this was significantly prevented with PLX3397 (P < 0.001, P < 0.0001) (two-way ANOVAs with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 4–6/group). (I–N) Analysis of striatal glia revealed a significant R6/2 genotype effect (P < 0.01) on Olig2+ number (×20; I and J) coincident with a significant increase in R6/2 myelinated (MBP+ ×20; K and L) white matter area coverage (P < 0.01) that is normalized with PLX3397 (P < 0.05) (two-way ANOVAs with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 4–6/group). Quantification of integrated S100β+ signal density (×20; M and N) revealed extensive astrogliosis in the R6/2 striatum (P < 0.0001) that was prevented with PLX3397 (P < 0.0001) (two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 5–6/group). Significance is denoted by *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Error bars indicate SEM.