Figure 10.
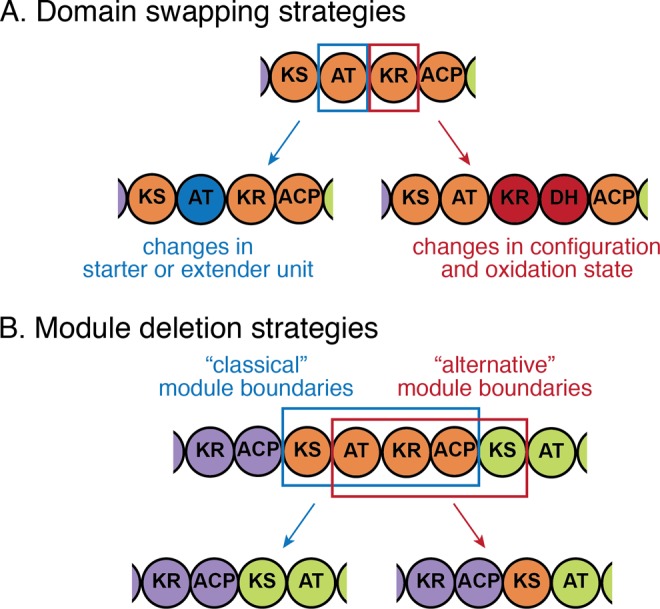
Alternative splice points for PKS engineering. (A) Two domain swapping strategies can lead to predictable changes in the structure of biosynthesized molecule: AT domain swaps affect the choice of starter or extender unit (malonyl-CoA, methylmalonyl-CoA, or other), whereas reductive loop swaps alter the configuration and oxidative state of the newly added extender unit. For both types of domain swaps, conserved regions were identified that can be used as splice points.205,210 (B) “Classical” module boundaries match the boundaries of unimodular proteins and correspond to the functional unit of chain elongation (KS and downstream ACP) and subsequent modification (reductive loop). “Alternative” module boundaries break the functional unit of chain elongation but preserve chain translocation unit (KS and upstream ACP), along with the reductive loop that determines the oxidative state of the translocated substrate.39 Both “classical” and “alternative” module boundaries have been successfully used for module deletion (shown here), as well as module swapping and insertion.78,90,206 KS, ketosynthase; AT, acyltransferase; ACP, acyl carrier protein; KR, ketoreductase; DH, dehydratase.
