Figure 2.
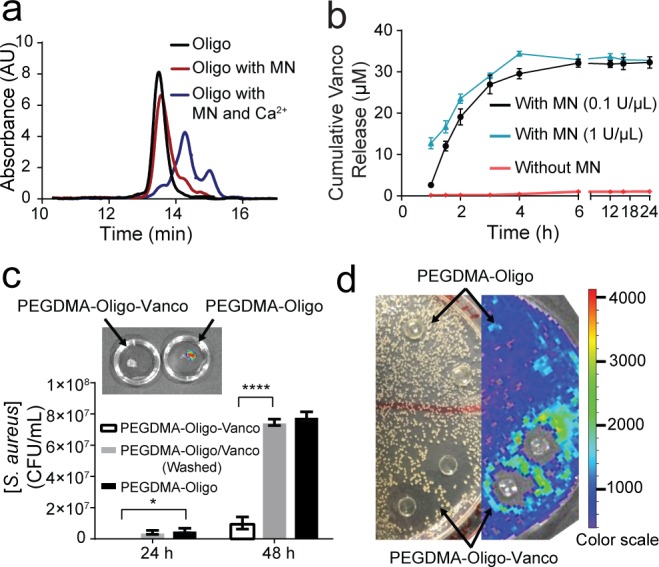
MN-triggered oligo cleavage and the antibacterial activities of PEGDMA-Oligo-Vanco hydrogel in vitro. (a) GPC traces of intact oligo (black) and oligo upon treatment with MN with (blue) and without (red) Ca2+. (b) Cumulative vancomycin (Vanco) release from PEGDMA-Oligo-Vanco hydrogel incubated with (black and blue) and without (red) MN. Differences at all given time points were significant (p ≤ 0.0001). (c) Total bacterial counts after 24 and 48 h of Xen-29 S. aureus culture in LB media containing PEGDMA-Oligo-Vanco, washed PEGDMA-Oligo/Vanco, or PEGDMA-Oligo hydrogels (n = 3; inset, corresponding IVIS image of the PEGDMA-Oligo-Vanco and PEGDMA-Oligo hydrogels retrieved after 48 h in S. aureus culture). (d) Photograph (left) and IVIS image (right) of an LB agar plate of Xen-29 S. aureus culture 24 h after placement of PEGDMA-Oligo-Vanco and PEGDMA-Oligo hydrogel discs (n = 2 shown) over the agar plate. Error bars represent standard deviations. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA).
