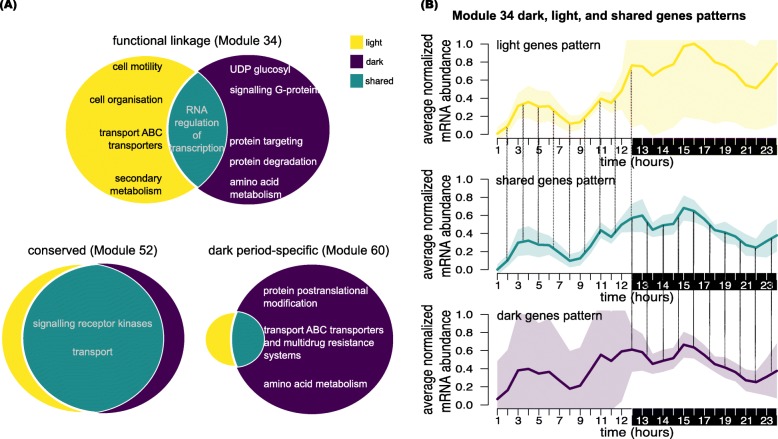
Fig. 4.
Functional linkage, conserved and condition-specific modules of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii between light and dark condition a Module types identified by ManiNetCluster, using an algal diurnal dataset [42] with light-period and dark-period transcriptomes treated as independent experiments. Example modules are shown: (1) Module 52 - a conserved module in which the proportion of shared genes is high; (2) Module 60 - a dark specific module in which the proportion of dark period genes is high; (3) Module 34 - a functional linkage module in which the proportion of shared genes is low and the proportion of light period genes and dark period genes are approximately equal. Functional enrichment for each were generated using MapMan (a tool for functional annotation based on gene ontologies designed for photosynthetic organisms) [46]. b Expression patterns of example functionally linked modules: Expression patterns of light, dark, and shared genes of module 34 are shown. The shared genes (shown in teal) correlate with light genes (yellow) in light condition (13 first time points) and with dark genes (purple) in dark condition (15 last time points) as indicated by vertical dashed lines. Note that the dark genes in light condition and the light genes in dark condition are not identified as the error bar (light purple shading in 13 first time points and light yellow shading in 15 last time points) are too large; this indicates that the shared genes serve as a bridge connecting the gene expression from light to dark conditions. The light and dark periods are shown with shading on the x axis. Complete module data are in Tables S1 and S2