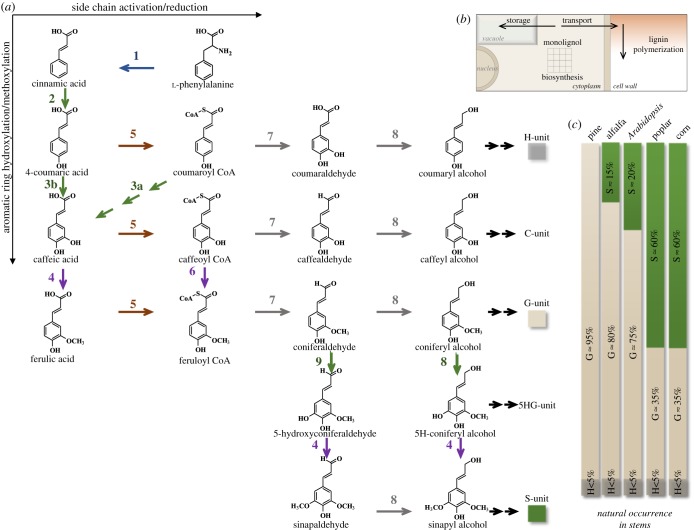
Figure 2.
Pathways to monolignols and lignin diversity in plants. (a) A schematic depiction of the enzymatic reactions involved in monolignol biosynthesis from l-phenylalanine. The different types of reaction are colour-coded: blue, deamination; green, hydroxylation; purple, O-methylation; brown, CoA activation; grey, reduction. Enzymes are: 1, l-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL); 2, cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase (C4H); 3a, the SS (figure 3) involving hydroxycinnamoyl CoA: shikimate hydroxycinnamoyl transferase (HCT), coumaroyl shikimate 3′-hydroxylase (C3′H) and CSE; 3b, coumarate 3-hydroxylase (C3H); 4, caffeic acid/5-hydroxyconiferaldehyde 3/5-O-methyltransferase (COMT); 5, 4-hydroxycinnamate CoA ligase (4CL); 6, caffeoyl CoA 3-O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT); 7, cinnamoyl CoA reductase (CCR); 8, cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD); 9, ferulic acid/coniferaldehyde 5-hydroxylase (F5H). (b) Cellular sites of monolignol synthesis and accumulation; monolignols are synthesized in the cytosol, with some enzymes exhibiting membrane attachment (figures 3 and 4), some monolignol derivatives accumulate in the central vacuole and the bulk of the monolignol pool is targeted to the apoplast for polymerization to lignin. (c) Variation in lignin monomer composition between species. Data compiled from [7,8].