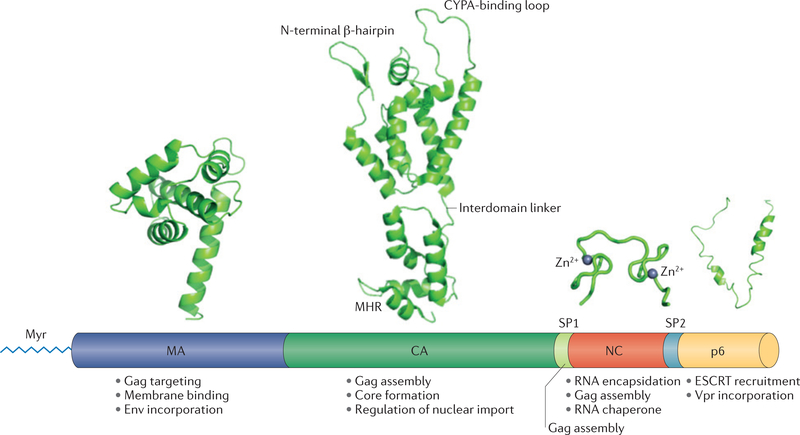
Figure 2 |. Gag structure and functions.
High-resolution structures of the major domains of Gag — matrix (MA), capsid (CA), nucleocapsid (NC) and p6 — are presented over a linear depiction of the Gag precursor polyprotein. The major functions of each Gag domain are indicated. MA (Protein Data Bank (PDB) accession 1HIW)37 is involved in Gag targeting and binding to the plasma membrane, and in incorporation of the envelope (Env) glycoprotein. Membrane binding requires amino-terminal myristylation (Myr). CA (PDB accession 2M8N)115 participates in Gag assembly, formation of the conical capsid core and regulation of the nuclear import of viral DNA. The CA N-terminal domain (CANTD) contains an N-terminal β-hairpin and a proline-rich loop that binds the host protein cyclophilin A (CYPA); the CA carboxy-terminal domain (CACTD) contains the major homology region (MHR). CANTD and CActd are connected by a short, flexible interdomain linker. Spacer peptide 1 (SP1) is involved in Gag assembly. NC (PDB accession 1BJ6)116 contains two zinc-finger domains; it participates in Gag assembly and RNA encapsidation, and serves as an RNA chaperone. p6 (PDB accession 2C55)8 is involved in recruitment of the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) components and in Vpr incorporation.