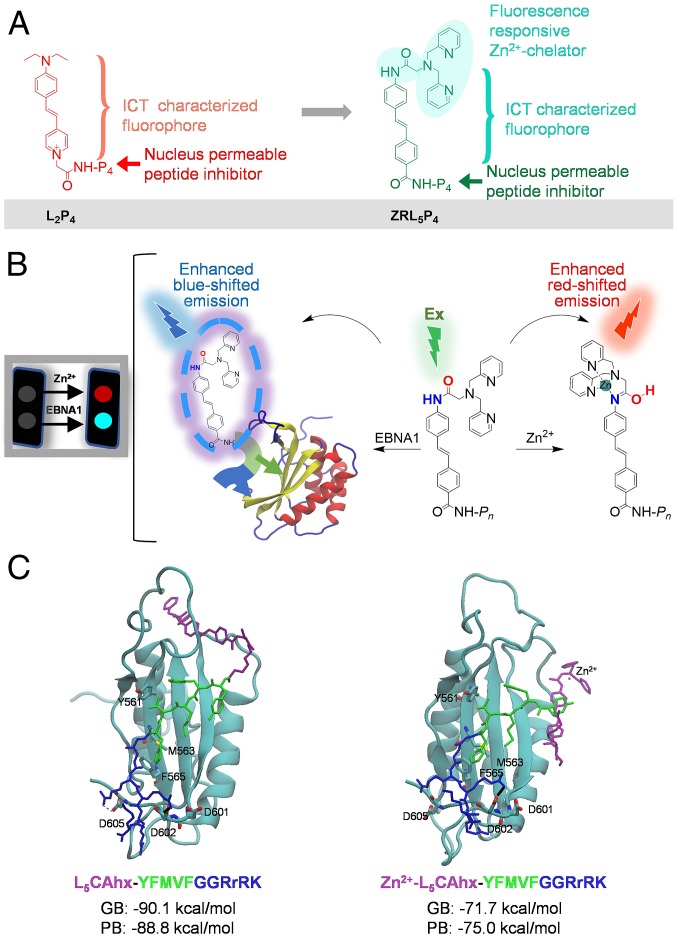
Fig. 1.
Chemical, fluorescent, and EBNA1-binding characteristics of the Zn2+ chelator EBNA1 probe ZRL5P4. (A) Chemical structures of L2P4 and ZRL5P4. (B) Schematic illustration of the emission response of ZRL5P4, binding to Zn2+ and EBNA1. (C) Representative conformations of ZRL5P4 and Zn2+-ZRL5P4 in the MD simulations. The calculated generalized Born (GB) and Poisson–Boltzmann (PB) values represent the binding free energy between EBNA1 and ZRL5P4 or Zn2+-ZRL5P4.