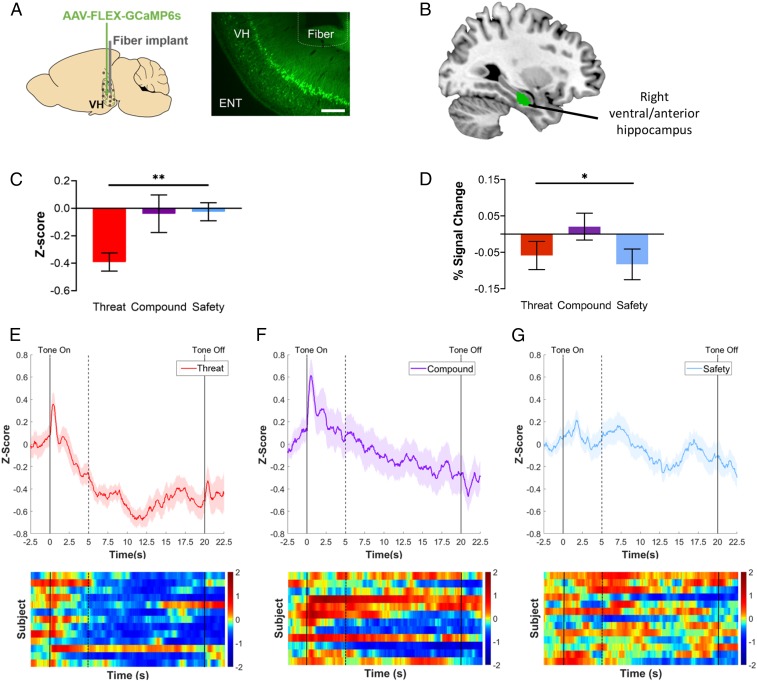
Fig. 2.
Cross-species ventral hippocampal responses. (A) Schematic of fiber photometry targeted to ventral hippocampus in mice. (Left) Schematic of injection site for AAV-FLEX-GCaMP6s and fiber placement (ventral hippocampus). (Right) Representative example of GCaMP expression and fiber placement in ventral hippocampal cell bodies. (10× magnification, scale bar, 200 μm.) ENT, entorhinal cortex; VH, ventral hippocampus. (B) Ventral hippocampus ROI in humans. The right ventral/anterior hippocampus ROI examined in the present study (green) was obtained from ref. 66. (C) Neural activity by condition in mice. Mean z-score of calcium signal recorded from ventral hippocampal neurons showed a significant linear contrast in which neural activity was highest during the threat cue and lowest during the safety cue, P = 0.008, η2 = 0.18. Threat condition: n = 13; compound condition: n = 12; safety condition: n = 13. (D) Task-related ventral hippocampal response in humans. Mean percent signal change extracted from the right ventral hippocampus ROI showed a significant quadratic contrast indicating that activation in the right ventral hippocampus was higher during the compound cue relative to both the threat cue and the safety cue, n = 50, P = 0.020, ηp2 = 0.11. (E–G) Fiber photometry traces recorded from cumulative ventral hippocampus. Traces of z-scored calcium signal and corresponding heatmaps for the threat condition (E), compound condition (F), and safety condition (G). Solid lines indicate tone onset (0 s) and offset (20 s). Dashed line indicates tone onset-induced activity for corresponding timeseries data. All error bars show ± 1 SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.