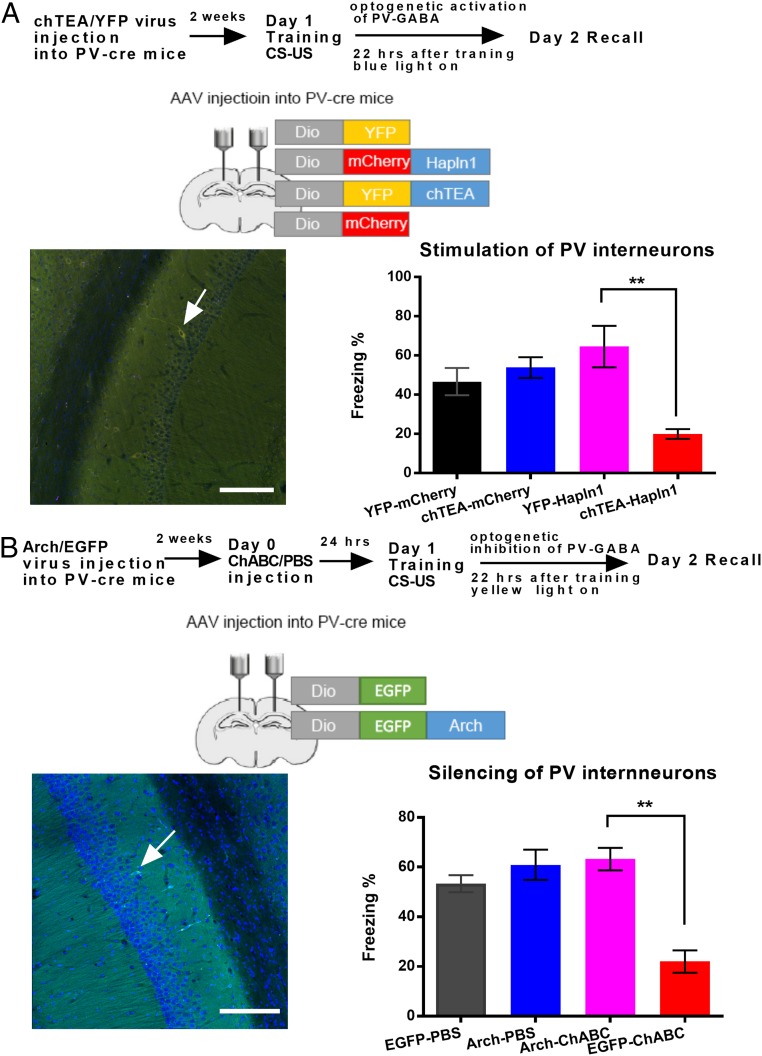
Fig. 6.
Optogenetic manipulation of PV interneurons and PNN on fear memory consolidation. (A, Top) Schematic drawing of the experimental design for contextual fear conditioning, indicating the effect of PNN on the optogenetic activation of PV interneurons. (A, Left) Schematic drawing of the virus injection on the hippocampus. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (A, Right) Contextual fear memory test after optogenetic activation of PV interneurons in the mCherry- and Hapln1-treated groups. n = 8 for YFP-hapln1 and chTEA-hapln1; n = 11 to 12 for YFP and chTEA-mCherry. (B, Top) Schematic drawing of the experimental design for contextual fear conditioning, indicating the effect of PNN on the optogenetic inhibition of PV interneurons. (B, Left) Schematic drawing of the virus injection on the hippocampus. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (B, Right) Contextual fear memory test after optogenetic inhibition of PV interneurons in the PBS- and ChABC-treated groups. n = 8 for Arch-ChABC and n = 11 for EGFP-ChABC; n = 10 for EGFP-PBS for Arch-PBS. All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Significance was tested by 1-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. **P < 0.01.