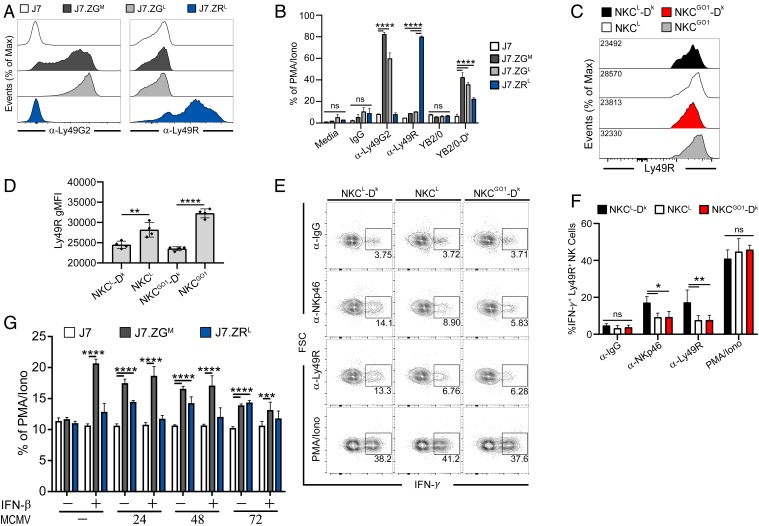
Fig. 3.
Ly49G2 and Ly49R receptors specifically bind MHC I Dk. (A) Surface expression of chimeric Ly49 receptors on J7 reporter cells, as determined by anti-Ly49G2 (4D11) and anti-Ly49R (12A8) mAb staining of J7.ZGM, J7.ZGL, or J7.ZRL reporter cells. (B) Reporter cells were stimulated with plate-bound mAbs or target cells. (C) Representative histograms of Ly49R expression by splenic NK cells. (D) Quantification of Ly49R gMFI from C. (E) Representative intracellular IFN-γ staining of spleen NK cells from uninfected NKCL-Dk, NKCL, and NKCGO1-Dk mice following stimulation with the indicated plate-bound mAbs or PMA/ionomycin. (F) Percentages of splenic Ly49R+ NK cells that express IFN-γ from E. (G) Reporter cells were cocultured for 12 h with infected M2-10B4 cells pretreated with IFN-β 16 h before coculture, as indicated. Target cells were infected for the indicated times prior to coculture with reporter cells. Data in A and B are representative of 3 to 5 independent experiments with 2 to 5 samples per group. Data in C and D are representative of 3 experiments with 3 to 4 mice per group. Data in E and F are representative of 2 independent experiments with 4 mice per group. Data in G is representative of 2 experiments with 3 to 6 samples per group. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.