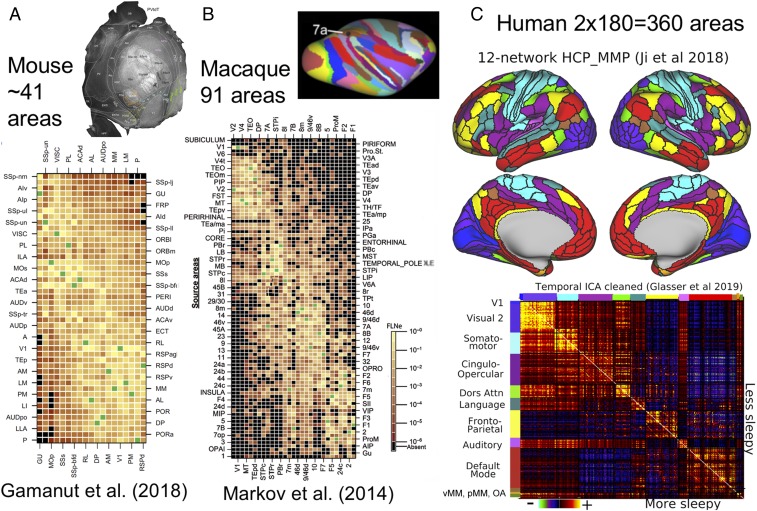
Fig. 5.
Parcellated cortical connectivity matrices. (A) A 19 × 47 weighted connectivity matrix for the mouse, including 7 subareas of SSp. Adapted from ref. 27, with permission from Elsevier. (B) A 29 × 91 weighted connectivity matrix for the macaque. Adapted from ref. 31 by permission of Oxford University Press. (C, Top) A 12-network resting-state network representation of the human HCP_MMP1.0 parcellation (42). (C, Bottom) A functional connectivity matrix from 449 HCP subjects. OA, orbital affective; pMM, posterior multimodal; vMM, ventral multimodal. The published functional connectivity matrix (42) has been cleaned using tICA (43) and here shows the difference between potentially more sleepy (high mean resting-state tICA component RC1 amplitude; n = 241) below the diagonal and less sleepy (low mean RC1 amplitude; n = 208) above the diagonal, using a mean RC1 amplitude of 6 as the threshold. Data for C are available at https://balsa.wustl.edu/kN69P.