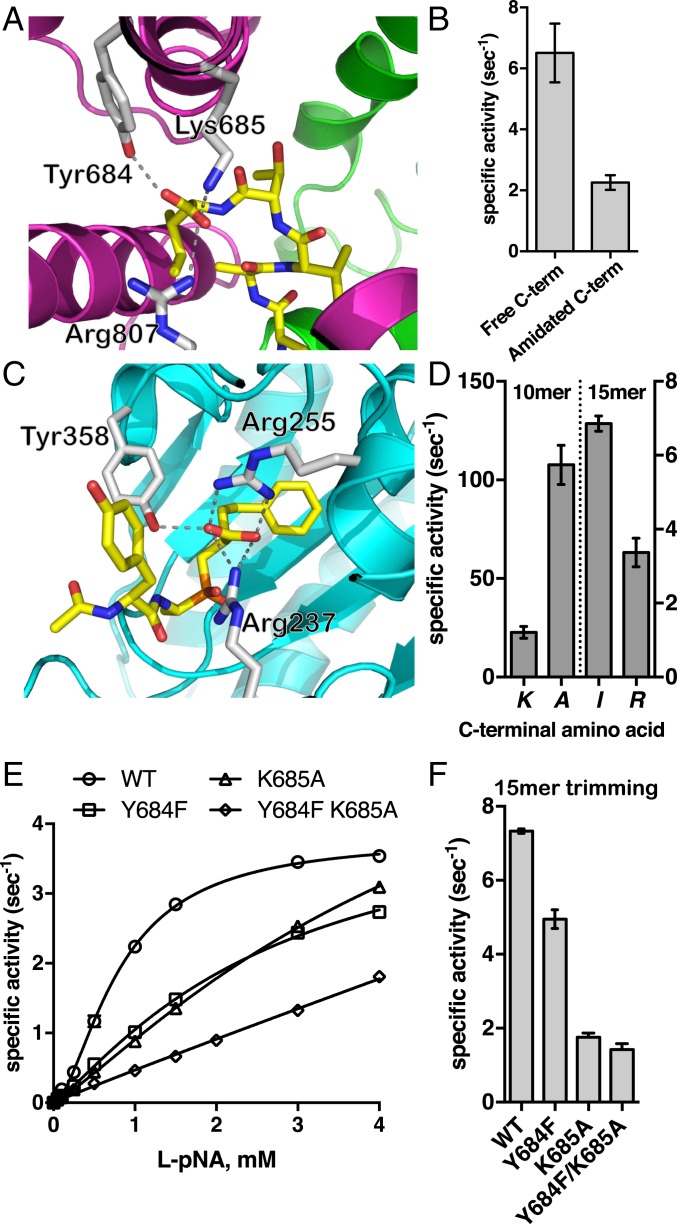
Fig. 3.
(A) Interactions between the C terminus of bound 15-mer peptide analog and ERAP1. The enzyme is shown in cartoon representation color-coded by domain as in Fig. 1. The peptide is shown as yellow sticks, oxygen atoms are in red, and nitrogen atoms are in blue. Key ERAP1 residues that participate in the interactions are shown as gray sticks. (B) Effect of amidation of the C terminus on the trimming rate of 15-mer peptide LLRIQRGPGRAFVTI. (C) Schematic representation of a phosphinic transition state analog in the catalytic site of carboxypeptidase A1 (PDB ID code 4UEF). Interactions between amino acids in ERAP1 or carboxypeptidase A1 and the C-terminal group of the ligand are indicated by dotted lines. (D) Effect of substituting the C-terminal residue of 10-mer and 15-mer peptide with Ala and Arg, respectively, on trimming rates by ERAP1. (E) MM analysis of ERAP1 variants carrying mutations of key residues of the C terminus recognition site on the hydrolysis of substrate L-pNA. (F) Trimming rate of 15-mer peptide LLRIQRGPGRAFVTI by wild-type ERAP1 and ERAP1 variants Y684F, K685A, and Y684F/K685A.