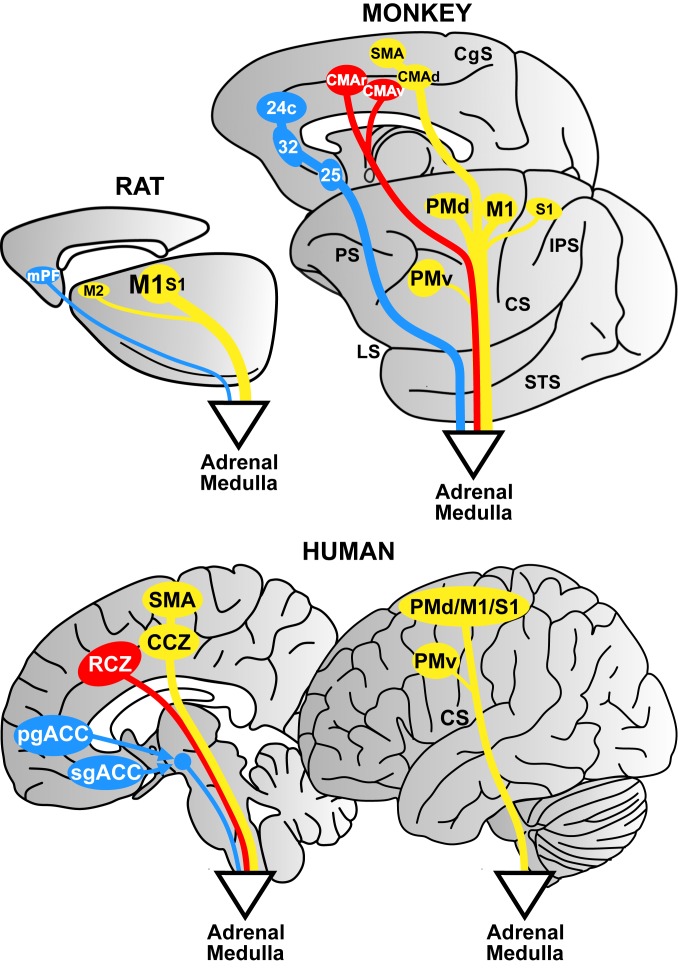
Fig. 6.
Cortical origin of top-down influences over the adrenal medulla: rat–nonhuman primate–human comparison. Motor networks are in yellow, cognitive networks are in red, and affective networks are in blue. Rat: Cortical output to the adrenal medulla originates largely from M1 on the lateral surface of the hemisphere. Monkey and human: Cortical output to the adrenal medulla originates from a motor network (M1, PMd, PMv, and S1 on the lateral surface and the SMA and CMAd on the medial wall [mirror image]). The medial wall motor areas are absent in the rat. Output from a cognitive network arises from the CMAr and CMAv on the medial wall (comparable to the RCZ of humans). This cognitive network is absent in the rat. Both the motor and cognitive influences are mediated, at least in part, by the corticospinal system. An affective network consists of areas 24c, 32, and 25 on the rostral medial wall in the monkey and corresponds to the pgACC and the sgACC in humans. The affective influence is mediated by various subcortical routes. Abbreviations are as in Figs. 2 and 3.