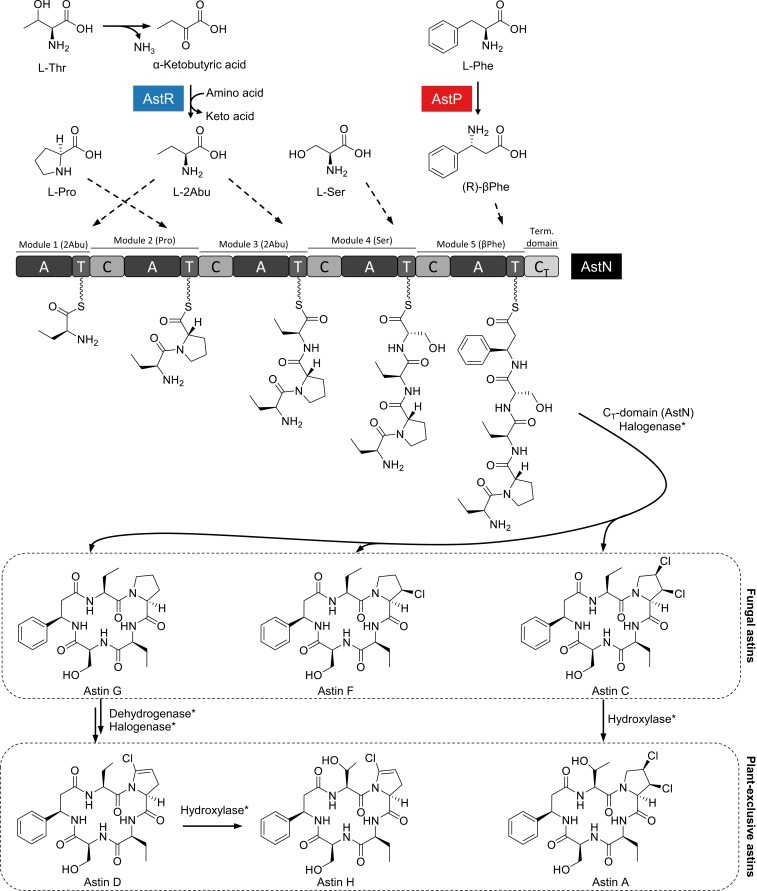
Fig. 3.
Biosynthesis model for the main astin variants. In conjunction with in silico analysis of the NRPS adenylation (A) domains and gene function prediction of the ast biosynthetic gene cluster, a biosynthesis model has been deduced. AstR and AstP are proposed here to supply the nonproteinogenic building blocks 2Abu and βPhe, respectively. The NRPS AstN assembles 5 building blocks to a macrocyclic pentapeptide. Dotted line arrows indicate incorporation by the A domains. The products released from AstN are proposed to be the fungal astins G, F, and C, which differ in the degree of chlorination. The plant-exclusive variants A, D, and H likely derive from the fungal astins as a result of a symbiosis between host and endophyte. Asterisk (*) denotes that the enzymes involved in tailoring of the astins are unknown.