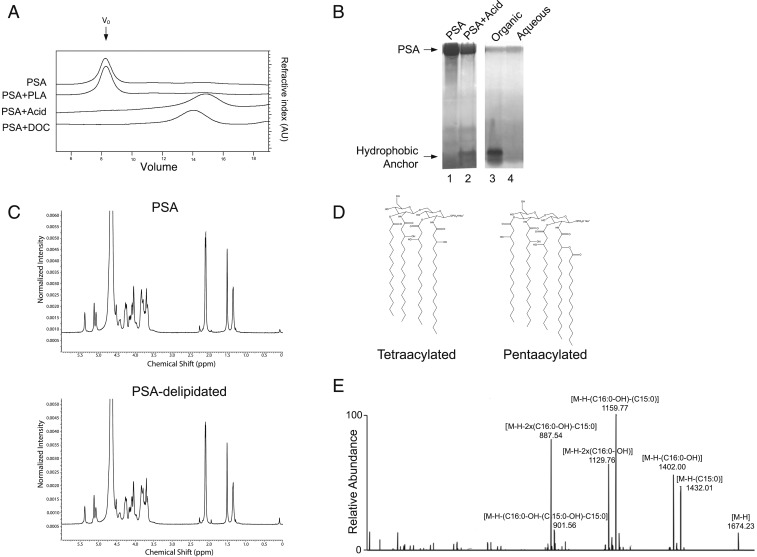
Fig. 5.
PSA contains a hydrophobic lipid anchor. (A) Gel filtration of 0.2-mg aliquots of PSA on a Superose 6 10/300 GL column running at a 0.5-mL/min flow rate. The elution profiles, from top to bottom, show untreated PSA, PSA treated with phospholipase A2 (PLA), PSA treated with 2% acetic acid, and PSA run in 1% deoxycholate (DOC) buffer. (B) Zinc gel analysis of untreated PSA (lane 1), PSA treated with 2% acetic acid solution at 90 °C for 3 h (lane 2), and the organic (lane 3) and aqueous (lane 4) phases of chloroform/methanol extraction of acid-treated PSA. Release of the acid-labile hydrophobic lipid moiety was detected in the organic phase. (C) 1H-NMR analysis of PSA and delipidated PSA showed no difference in the carbohydrate structure. (D) Representative species of B. fragilis lipid A, such as tetraacylated-monophosphorylated (combined carbon chain length = 64, molecular weight [MW] = 1421.0) and pentaacylated-monophosphorylated (combined carbon chain length = 80, MW = 1675.2), form on the diacylglucosamine backbone. A phosphate group may be attached at C1 or C4′ position, and some of acyl chains may be branched. (E) MS/MS fragmentation assigned the acyl chains as saturated or monohydroxylated C15–C17 fatty acids.