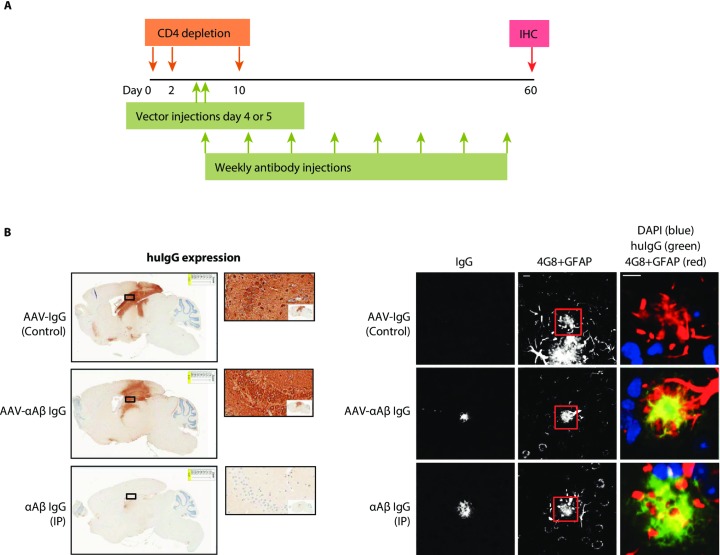
Fig 2. Antigen binding by AAV-αAβ IgG in a mouse model of amyloid plaque deposition.
A) Study design for intracranial (AAV-αAβ IgG or AAV-IgG Control) and peripheral dosing (αAβ IgG). APP mice were immunotolerized by CD4 T-cell depletion between days 2–10. AAV-αAβ IgG, or the isotype control vector AAV-IgG Control, were injected into the hippocampus bilaterally (2E10 GC per injection) at days 4–5. Purified αAβ huIgG was injected weekly, IP at 10mg/kg. After 8 weeks, 5um sagittal brain sections were collected and immunostained as indicated below. B) Expression of AAV-αAβ IgG or AAV-IgG Control. huIgG IHC revealed expression throughout the hippocampus and overlying cortex. Magnified ROIs (500um width) show detail of huIgG expression in neurons and in the neuropil of the hippocampus. Animals receiving antibody injected IP did not exhibit any expression in cell bodies. Images at right show IgG binding to plaques in frontal cortex. AAV-αAβ IgG and peripherally delivered αAβ IgG displayed clear binding to 4G8+ amyloid deposits, while the AAV-IgG Control did not display detectable binding. Scale bars are 10um.