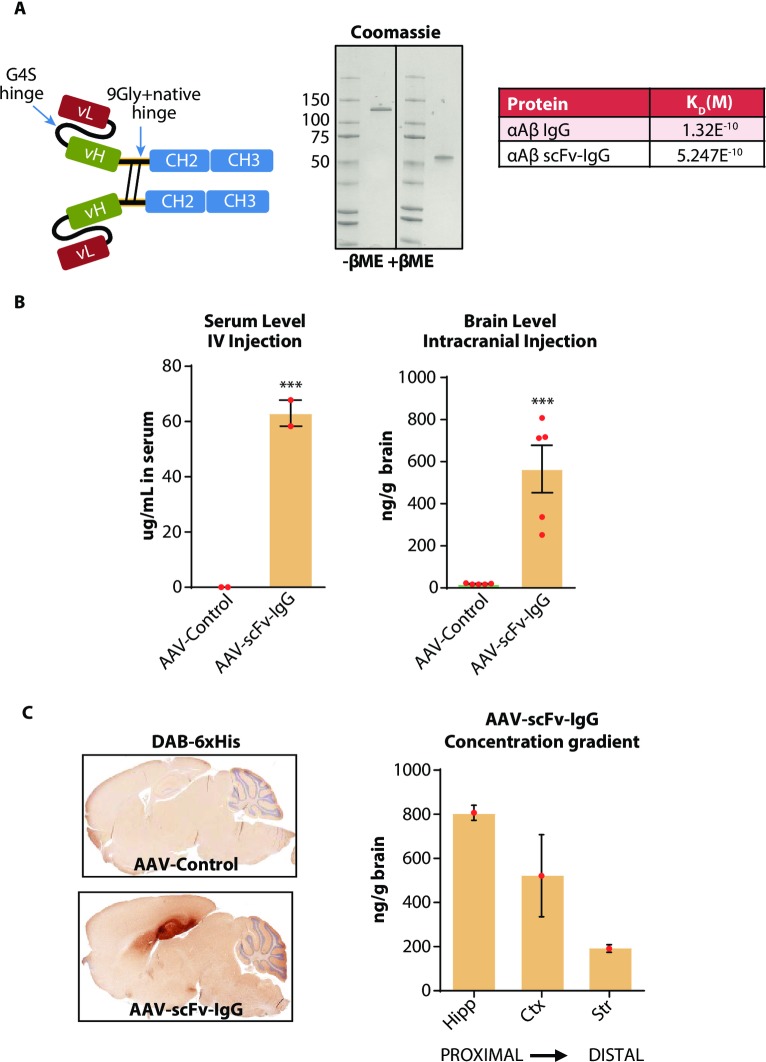
Fig 4. Construction and characterization of an AAV-scFv-IgG vector.
A) Schematic of the scFv-IgG design. The scFv-IgG used the variable regions of the murine anti-Aβ IgG [21] linked via 3 repeats of a flexible GGGGS linker sequence. The scFv was linked to the mouse IgG1 N297A Fc via a 9-Gly repeat linker. A 6xHis tag was added to the C-terminus. Reducing or non-reducing SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified scFv-IgG demonstrated purity and proper disulfide-dependent dimerization of the protein. Table at right compares antigen binding affinity of the scFv-IgG versus the IgG format. Affinity (M) was determined via SPR by flowing the scFv-IgG or IgG over immobilized Aβ1–42 fibrils at different molar concentrations to analyze binding kinetics. B) Left hand graph shows serum expression of the AAV-scFv-IgG as measured by antigen ELISA one month following peripheral injections of AAV into C57BL/6 mice. Vector was delivered by IV injection of 1E12 total GC. Right hand graph shows brain expression of the AAV-scFv-IgG as measured by antigen ELISA 1 month following hippocampal injection of 2E10 total GC of AAV into C57BL6 mice. ***p<0.001, unpaired Students t-test, n = 5 mice per group for intracranial injection, 2 mice per group for IV injection. C) DAB-6xHis immunohistochemistry on sagittal sections of mouse brain taken from the same animals as in (B, right) demonstrating hippocampal targeting of the vector, and transduction throughout the hippocampal formation. Graph to the right shows ELISA-based quantification of scFv-IgG in different brain regions after bilateral hippocampal injection of 1E10 GC of AAV-scFv-IgG. One month following AAV injection, brain regions from 3 mice were dissected and expressed protein was quantified by antigen ELISA for each brain region, with PBS-injected brain homogenate used to subtract background signal. Hipp = hippocampus. Ctx = overlying cortical regions. Str = striatum.