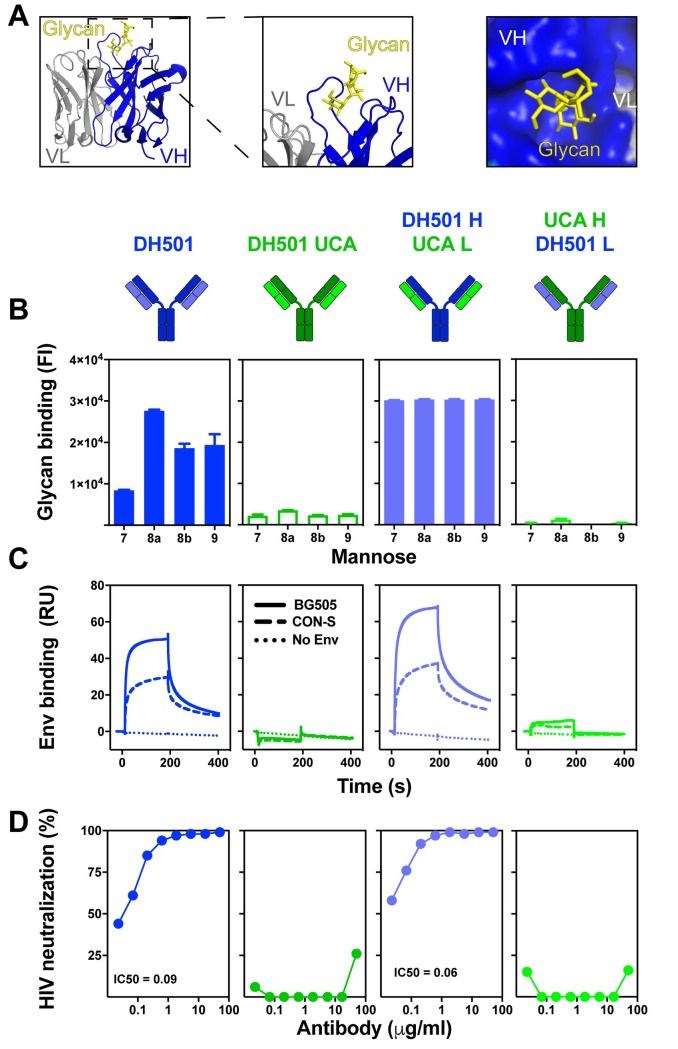
Fig 1. DH501 heavy chain somatic mutations, but not light chain mutations, are required for glycan reactivity and trimeric HIV-1 envelope recognition.
(A) Crystal structure of DH501 Fab (PDB: 5T4Z) bound to the terminal mannose residues of the D2 arm of Man9GlcNAc2. The Fab is shown in cartoon form with the Man9GlcNAc2 shown by stick structures. Magnified images in the middle and right show mannose residues contacting only heavy chain amino acids (blue). Image created in Pymol [41]. (B) Antibody binding to Man7GlcNAc2 D1, Man8GlcNAc2 D1D3, Man8GlcNAc2 D1D2, Man9GlcNAc2, which are denoted as 7, 8a, 8b, and 9 respectively. Throughout Fig 1 functional data is shown for the antibody listed at the top of the column. Antibody functions were assessed for DH501 with somatic mutations in both the heavy and light chain (DH501), with no somatic mutations (DH501 UCA), with somatic mutations only in the heavy chain (DH501 H/ UCA L), and with somatic mutations only in the light chain (UCA H/DH501 L). The mean and standard error are shown for independent triplicate experiments. DH501 H/ UCA L reached the upper limit of detection (fluorescence intensity of 31,000). Positive binding based on negative control antibody binding is shown as a filled bar. Open bars indicate negative binding values. Positivity thresholds for 7, 8a, 8b, and 9 are 0.6x104, 0.90x104, 0.67x104, 0.64x104 respectively. (C) Binding of various DH501 IgG variants to soluble, cleaved HIV-1 CON-S and BG505 SOSIP gp140 envelope. Dotted lines show binding to blank flow cells as a negative control. Values are representative of two independent experiments. (D) In vitro HIV-1 pseudovirus neutralization of kifunensine-treated (Man9GlcNAc2-enriched) JR-FL in the TZM-bl neutralization assay. Neutralization titers (IC50 in μg/mL) are shown for antibodies that neutralized virus replication 50% or greater.