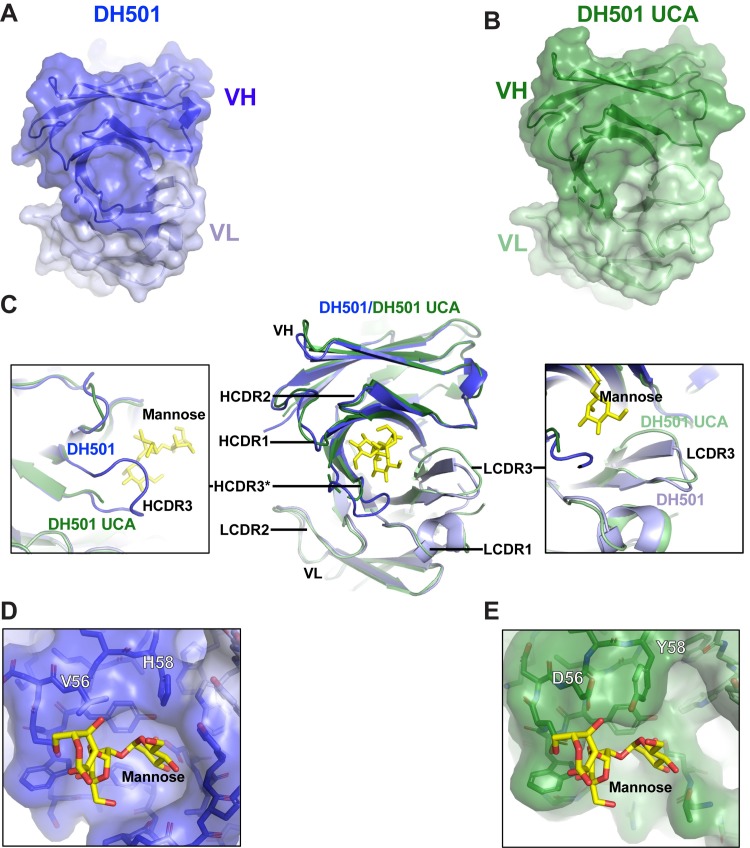
Fig 2. The crystal structure of the DH501 UCA.
(A,B) Top view of the crystal structures of (A) DH501 (blue; PDB: 5T4Z) and the inferred (B) DH501 UCA (green; PDB: 6P3B). The variable region of the heavy chain (VH) is shown in dark colors and the variable region of the light chain (VL) is shown in the light color. Portions of the HCDR3 in DH501 UCA were disordered, therefore, HCDR3 was omitted in the surface representation of the Fv structure. (C) A superposition of the Fv regions of the DH501 UCA (dark green heavy chain, light green light chain) and mature DH501 (dark blue/light blue). Inserted into the DH501 glycan-binding cavity is the stick structure of the terminal mannose on the D2 arm of Man9GlcNAc2 (yellow sticks). Zoomed in views of the HCDR3 and LCDR3 are shown in the boxes on the left and right side respectively. The disordered HCDR3 in DH501 is marked with asterisks. (D, E) Zoomed-in view of the glycan-binding cavity in (D) DH501 and (E) DH501 UCA antigen binding sites. Somatic mutation at position 56 and 58 are labeled with the corresponding amino acids. Note the side chain of Y58HFWR3 pointing down into the glycan-binding cavity as compared to H58 that forms a smooth, round-shaped roof of the cavity with its side chain oriented differently. Image created in Pymol [41].