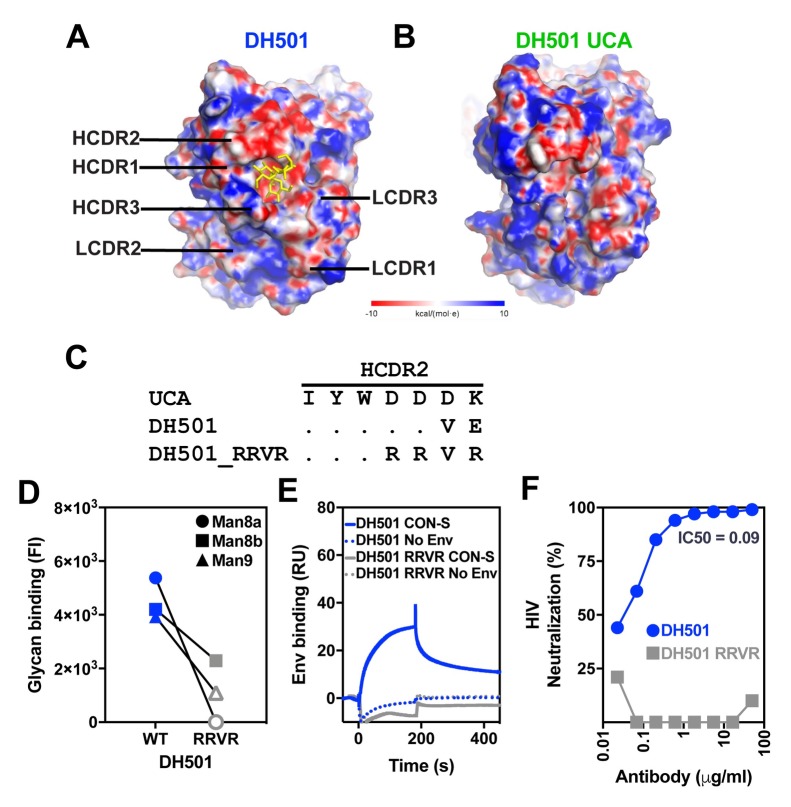
Fig 5. The negatively charged amino acid patch in HCDR2 is required for HIV-1 Env trimer binding.
(A, B) The electrostatic surface potential of (A) DH501 and (B) the DH501 UCA. The glycan binding pocket of the DH501 antibody has a negative charge. The terminal mannose residues of the D2 arm of Man9GlcNAc2 are shown in yellow. The electrostatic potentials are oriented with the paratope facing towards the viewer. (C) Amino acid alignment of HCDR2 of DH501 and the DH501 UCA. Dots indicate identical residues. The negatively-charged residues within the HCDR2 of DH501 were changed to positively-charged arginine residues (RRVR). (D) DH501 wildtype (WT) and the DH501_RRVR variant (RRVR) IgG binding to high mannose glycans in a custom luminex assay. The mean of 3 independent experiments is shown. Positive glycan binding values are shown as filled symbols. Positivity threshold for 7, 8a, 8b, and 9 was 1.8x103 for each glycan. (E) DH501 and DH501_RRVR IgG binding to soluble, trimeric CON-S SOSIP gp140s (solid line). Dashed lines show binding magnitudes in the absence of Env. Images are representative of two independent experiments. (F) DH501 and DH501_RRVR IgG in vitro HIV-1 neutralization of Man9GlcNAc2-enriched JR-FL.