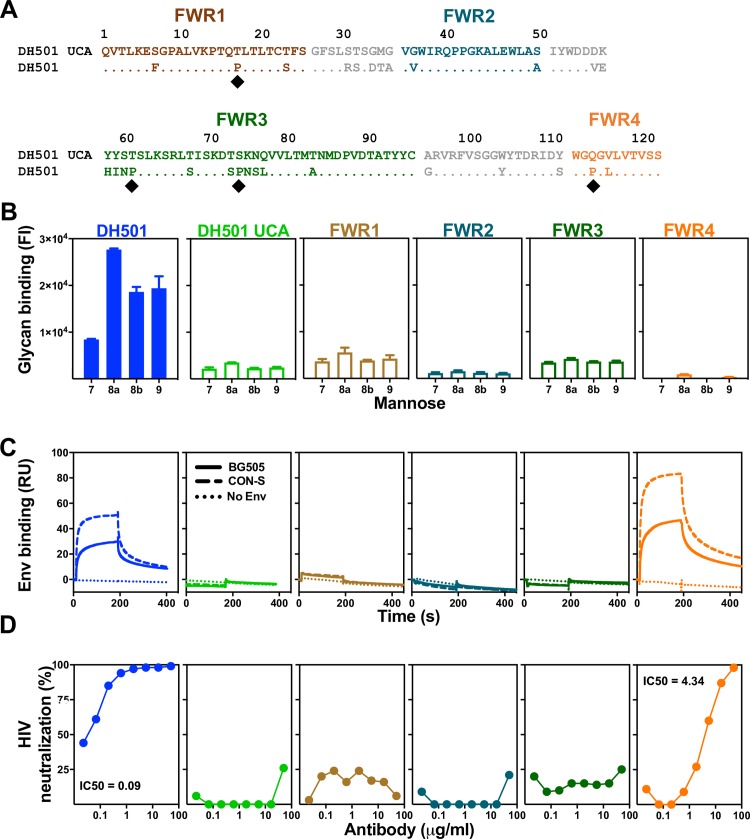
Fig 6. Somatic mutation of HFWR1, HFWR 2, and HFWR 3 is required for glycan reactivity and HIV-1 Env reactivity.
(A) ClustalW alignment of amino acids of DH501 and DH501 UCA VH. Identical residues are shown as dots. HFWRs are denoted based on the IMGT definition and color-coded. Black diamonds below the sequence alignment denote somatic mutations that introduce a proline substitution in HFWRs. (B) Binding of DH501 HFWR reverted antibodies to Man7GlcNAc2 D1 (7), Man8GlcNAc2 D1D3 (8a), Man8GlcNAc2 D1D2 (8b), Man9GlcNAc2 (9). The reverted antibodies are color-coded the same throughout B-D. Mean values + standard error are shown for triplicate experiments. Positive glycan binding based on negative control antibody binding is shown as a filled bar. Open bars indicate negative binding values. Positivity thresholds for 7, 8a, 8b, and 9 are 0.6x104, 0.90x104, 0.67x104, 0.64x104 respectively. (C) DH501, DH501 UCA, and HFWR-reverted IgG binding to CON-S SOSIP gp140 Env trimers (dashed line), BG505 6R.SOSIP.664 Env trimers (solid line), or buffer only was determined by SPR. Representative data from two independent experiments are shown. (D) In vitro HIV-1 neutralization of kifunensine-treated, Man9GlcNAc2-enriched JR-FL in the TZM-bl assay. IC50 neutralization titers are shown in μg/mL as in Fig 4D.