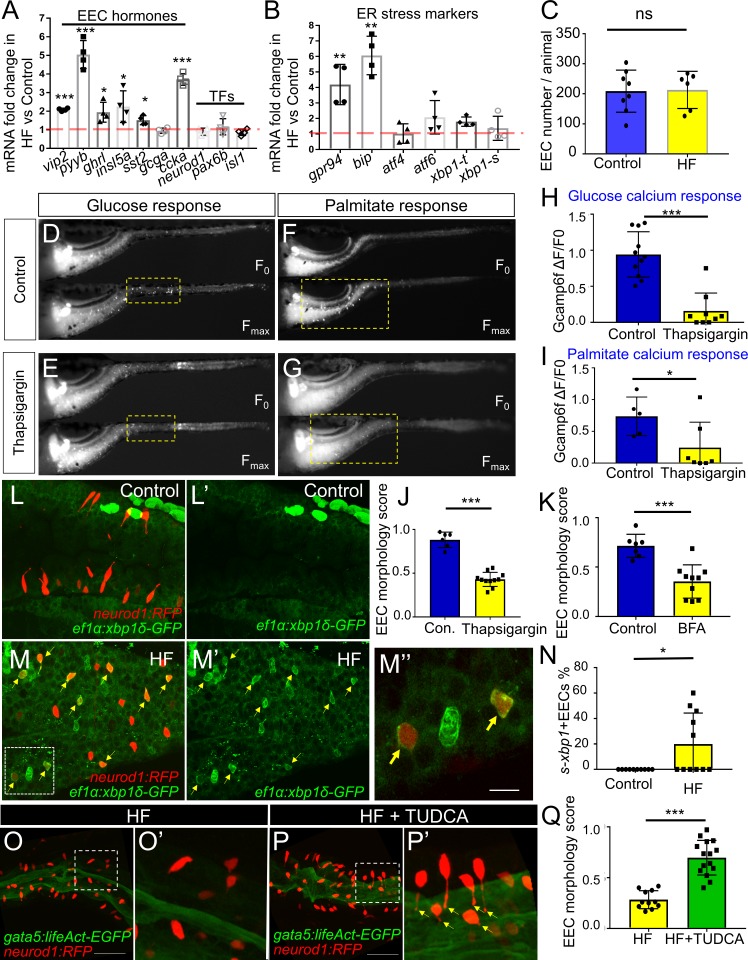
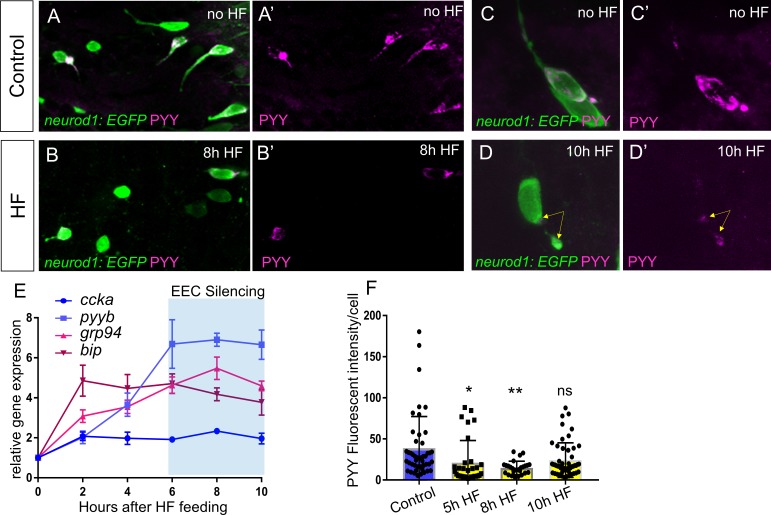
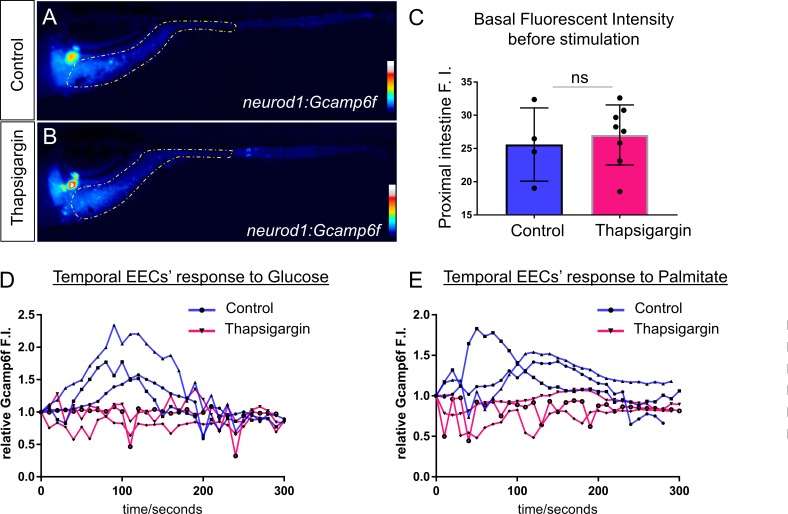
Figure 6. Activation of ER stress following high fat feeding leads to EEC silencing.
(A–B) Quantitative real-time PCR measurement of relative mRNA levels from dissected digestive tracts in control and 6 hr high fat (HF) meal larvae at 6dpf (n = 4 biological replicate pools of 20 fish per condition). The plot indicates the fold increase of relative mRNA levels of indicated genes. (C) Quantification of total EEC number in control (n = 8) and 6 hr HF fed larvae (n = 6). (D–G) Representative images of the EEC calcium response to glucose or palmitate stimulation in control (D, F) and 2 hr thapsigargin (ER stress inducer, 1 µM) treated larvae (E, G). (H, I) Quantification of the EEC calcium response toward glucose (H) and palmitate (I) in control and 2 hr thapsigargin (1 µM) treated larvae. (J–K) Quantification of EEC morphology score in control and 10 hr thapsigargin (0.75 µM) or brefeldin A (BFA, 9 µM) treated larvae Tg(gata5:lifeAct-EGFP);Tg(neurod1:RFP) double transgenic line. (L–M) Confocal projections of control (J) and 6 hr HF fed (K) zebrafish intestines. The EECs are marked by Tg(neurod1:RFP), the activation of ER stress is marked by Tg(ef1α:xbp1δ-GFP) and DNA is stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). (L’–M’) Subpanel images showing the activation of ER stress in control (L’) and 6 hr HF fed (M’) zebrafish intestines. (M’’) Zoom in view of s-xbp1+ EECs that displayed typical closed morphology in HF fed zebrafish intestine. Yellow arrows in M, M’ and M’’ indicate EECs with xbp1 activation. (N) Quantification of s-xbp1+ EECs (%) in control and 6 hr HF fed zebrafish larvae. (O–P) Confocal projection of zebrafish intestine in 10 hours HF fed (O) and 10 hr HF fed treated animals receiving 0.5 mM TUDCA (P). EECs are marked with Tg(neurod1:RFP) and the apical region of the intestine is marked with Tg(gata5:lifeAct-EGFP). (O’–P’) Zoom view of EECs in indicated conditions. Yellow arrows in P’ indicate EECs’ apical extensions. (Q) Quantification of the EEC morphology score in zebrafish larvae following 10 hr of HF feeding and 10 hr of HF feeding with 0.5 mM TUDCA. Student t-test was performed for statistical analysis. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.