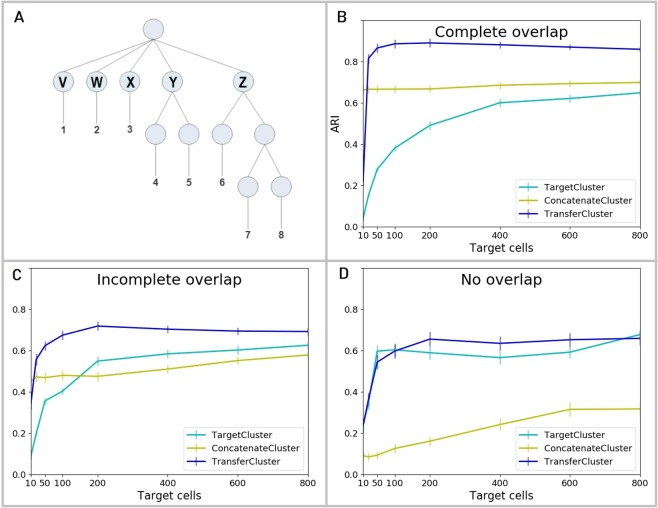
Figure 2.
scRNA-Seq simulation data description and results. (A) Count level single-cell RNA-Seq data is simulated according to a pre-defined hierarchical clustering structure with eight cell clusters (1-8) that are derived from five top level clusters (V - Z). Generated datasets are individually split up by randomly assigning the top node clusters V - Z to source or target. Three different settings are considered: 1. both source and target data contain cells from all top node clusters V - Z (Complete overlap), 2. three randomly selected top node clusters V - Z are chosen as common to both source and target, the other two are assigned to either one of source and target (Incomplete overlap) or 3. cells from two of the top node clusters form the target dataset and cells from the other three form the source (No overlap). (B) Clustering performances of the baseline methods, TargetCluster (clustering on the target dataset alone) and ConcatenateCluster (concatenating and clustering source and target data simultaneously), and the transfer learning approach (TransferCluster) when the clustering structures of source and target data are identical (Complete overlap). (C) Clustering performances of the baseline methods, TargetCluster and ConcatenateCluster and the transfer learning approach (TransferCluster) for an incomplete overlap between the cell clusters in source and target data (Incomplete overlap). (D) Clustering performances of the baseline methods, TargetCluster and ConcatenateCluster and the transfer learning approach (TransferCluster) for a setting with two exclusive target and three exclusive source top nodes and no cell types that appear in both sets (No overlap). Please note, that due to the sampling procedures described above, the number of top level nodes in the target datasets decreases from 5 in (B) to 4 in (C) and 2 in (D) and hence the performance of TargetCluster improves from (B–D). 95% confidence intervals are shown.