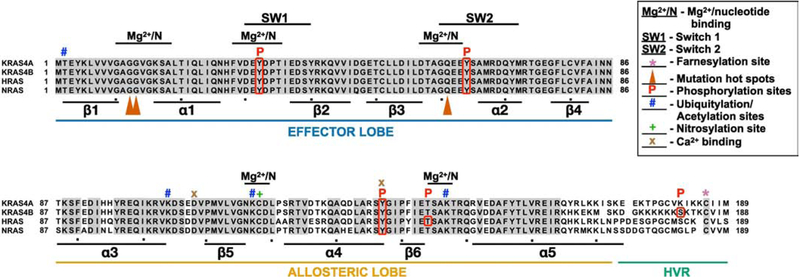
Figure 2. RAS family members.
RAS proteins were aligned with Clustal multiple alignment. KRAS4A and KRAS4B are derived from alternative splicing of the same gene resulting in different C-termini. Grey shading highlights residues that are identical in all four RAS proteins. RAS proteins can be divided into three functional regions: the effector lobe, allosteric lobe, and hypervariable region (HVR). SW1, switch 1 region (aa 30–40); SW2, switch 2 region (aa 60–76); Mg2+/N, magnesium and nucleotide binding regions, *, farnesylation site; , mutation hotspots; P, phosphorylation site; #, ubiquitylation or acetylation sites; +, nitrosylation site; x, Ca2+ binding sites. Alpha helices (α) and beta sheets (β) are indicated below lineup.