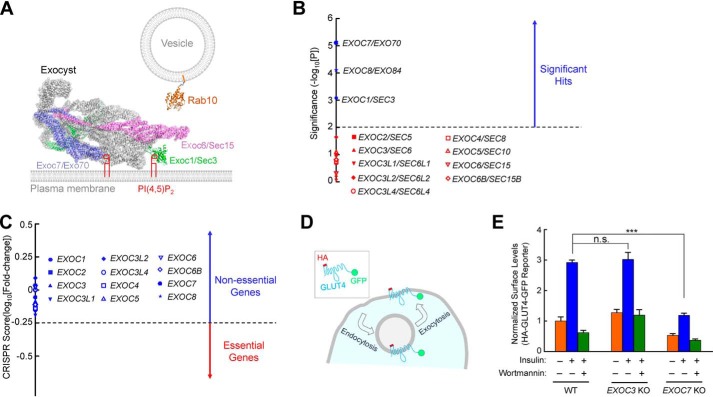
Figure 1.
Exocyst genes exhibit disparate phenotypes in a genome-wide CRISPR screen. A, illustration of Rab10 and exocyst anchored to membrane bilayers. The model is based on the structures of exocyst (PDB codes 5YFP and 3HIE) (22), and guanosine 5′-[β,γ-imido]triphosphate (GMP-PNP)-bound Rab10 (PDB code 5LPN) (67). The model was prepared using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific LLC, San Carlos, CA). Rab10, a known mediator of GLUT4 exocytosis (42, 51), interacts with the Exoc6/Sec15 subunit in yeast two-hybrid screens (36). The Exoc1 and Exoc7 subunits bind to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2), whereas Rab10 is anchored to the membrane through prenyl groups. Because the structures of the Rab10–exocyst complex and exocyst–membrane association are still unavailable, the positions of exocyst and Rab10 in the model are arbitrary. The proteins are shown to scale whereas the lipids and membranes are not. Besides Rab GTPases, the exocyst also interacts with other molecules, such as RalA and SNAREs (not shown) (29–31). B, ranking of exocyst genes in a genome-wide CRISPR screen of insulin-stimulated GLUT4 exocytosis in HeLa cells (42). The significance of a gene was calculated based on enrichment of its corresponding gRNAs in the screen using the MAGeCK algorithm (46). Genes above the horizontal cutoff line (p = 0.01) are significant hits. Only exocyst genes are shown. Of the 12 exocyst genes included in the CRISPR library, EXOC1, EXOC7, and EXOC8 were recovered as significant hits. C, a CRISPR score of a gene is calculated based on fold changes in the abundance of its corresponding gRNAs by comparing a passage control population of HeLa mutant cells (without stimulation or selection) with the initial CRISPR library. Genes with CRISPR scores below the horizontal cutoff line (CRISPR score, −0.25) are considered essential genes. Only exocyst genes are shown. CRISPR score ranking of all genes in the CRISPR library is shown in Table S2. D, diagram of the HA-GLUT4-GFP reporter used to monitor insulin-stimulated GLUT4 exocytosis. The GLUT4 reporter faithfully recapitulates trafficking of endogenous GLUT4 proteins (42, 68, 69). E, normalized surface levels of the GLUT4 reporter in WT and mutant HeLa cells. The cells were either left untreated or treated with 100 nm insulin for 30 min before surface GLUT4 reporters were labeled using anti-HA antibodies and APC-conjugated secondary antibodies. GFP and APC fluorescence was measured using flow cytometry. To inhibit insulin signaling, 100 nm wortmannin was added. Datasets were normalized to untreated WT cells. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. n = 3. ***, p < 0.001; n.s., not significant, p > 0.05.