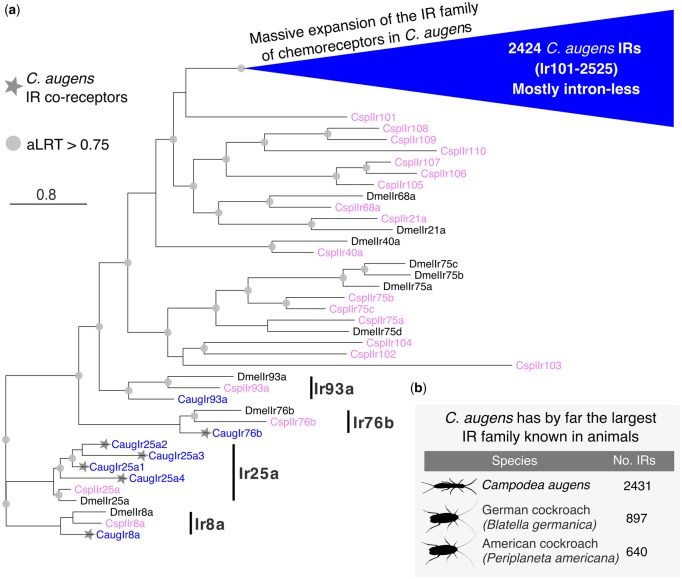
Fig. 4.
—Phylogenetic tree of the Campodea augens IR family. (a) The tree was rooted by declaring the Ir8a and 25a lineages as the outgroup, based on their basal positions within larger trees including the ionotropic glutamate receptors from which the IRs evolved. The blue triangle represents the massive expansion of C. augens IR family. Most of these 2424 IRs are intron-less, except for five lineages that have idiosyncratically gained introns (see supplementary fig. 10, Supplementary Material online for details). The C. augens (Caug) proteins are in blue, the Drosophila melanogaster (Dmel) proteins for the seven conserved IRs with orthologs in C. augens, as well as the Ir75 clade, are colored black, whereas the Calopteryx splendens (Cspl) proteins are colored purple. The four conserved lineages are marked with a black bar. Campodea augens IR coreceptors are marked with a star. The scale bar indicates substitutions per site. Gray circles indicate nodes with an approximate Likelihood-Ratio Test (aLRT) >0.75. (b) Table displaying the animal species with the largest repertoire of IRs. Campodea augens possesses by far the largest IR family known in animals to date. Silhouette images were obtained from PhyloPic (http://phylopic.org; last accessed March 10, 2019). All are under public domain.