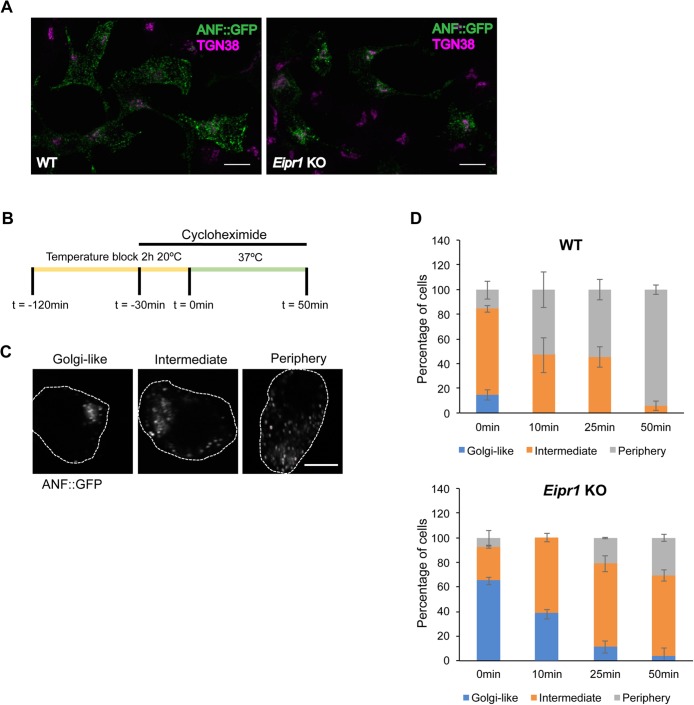
FIGURE 4:
DCV cargoes exit the TGN in Eipr1 KO cells. (A) Representative images of WT and Eipr1 KO 832/13 cells transfected with ANF::GFP and costained with anti-GFP and anti-TGN38 antibodies. In WT cells, ANF::GFP is distributed in cytoplasmic puncta, but in Eipr1 KO cells, ANF::GFP is restricted to perinuclear puncta. Not all cells in this field of view are transfected with ANF::GFP. Scale bars = 10 μm. (B) Schematic of the pulse-chase experiment. Cells transiently transfected with ANF::GFP were incubated at 20°C for 2 h to cause the accumulation of DCV cargoes at the TGN (pulse). Before the end of the temperature block (30 min), cyclohexamide was added to block protein translation. At the end of the temperature block, cells were returned to 37°C and incubated for various times (chase) before fixation and immunostaining. (C) Representative images of the cell categories used for qualitative assessment of TGN exit: 1) ANF::GFP concentrated at the TGN region (Golgi-like), 2) ANF::GFP distributed both at the TGN and at the cell periphery (Intermediate), or 3) ANF::GFP excluded from the TGN (Periphery). Scale bar = 5 μm. (D) Percentage of WT and Eipr1 KO cells with the indicated ANF::GFP distribution at the indicated time points. For each data point and genotype, 50–100 cells were counted blindly. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. The data shown for the WT are the same as shown in Supplemental Figure S5D of Cattin-Ortolá, Topalidou, et al. (2019) because these experiments were run in parallel with the same WT control.