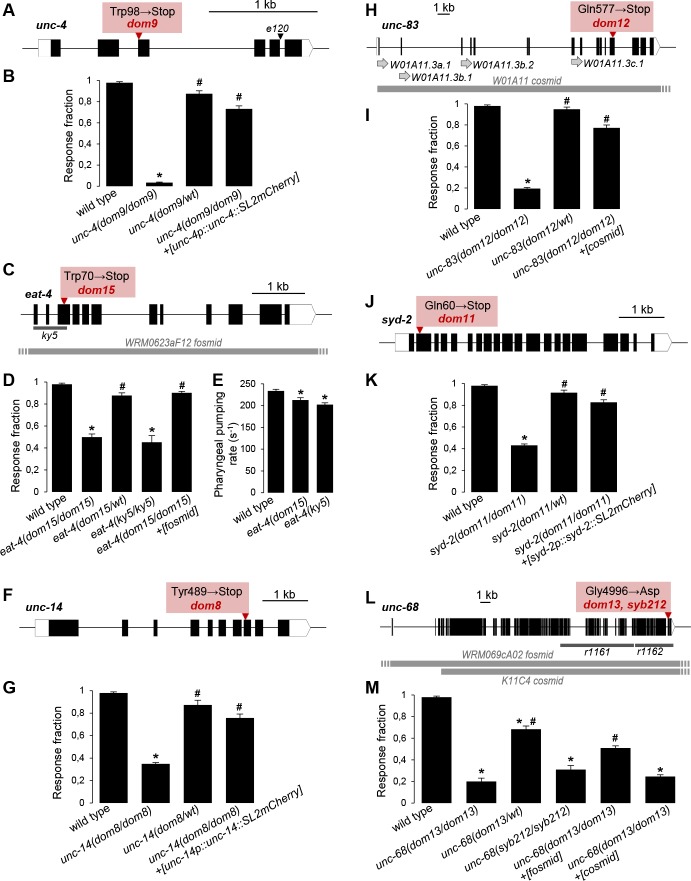
Fig 3. Mutations impairing FLP-evoked reversals.
A, C, F, H, J, L: Scheme representing new mutations recovered from the screen for defects in reversals induced by optogenetic activation of FLP (red box). Genes are schematized with exons (black boxes) and untranslated regions (white boxes). Additional alleles used in the present study are also depicted, as well as genomic regions contained in cosmids and fosmids (horizontal grey bars). Grey arrows indicate alternative transcriptional starts in the unc-83 gene (H). syb212 (generated by genome editing) encodes the same UNC-68(G4996D) mutation as dom13 (M). B, D, G, I, K, M: Fraction of blue light stimulation trials (61 W/m2) triggering a reversal response in adult [FLP::CoChR] animals. Results are presented as averages (bars) and SEM (error bars); n≥40 animals, each tested five times. E: Pharyngeal pumping rate assessed in adult animals of the indicated genotypes. Results are presented as averages (bars) and SEM (error bars). n≥40 animals, each scored over 20 s. One way ANOVAs indicated significant genotype effects in every situation. *, p < .01 versus wild type; #, p < .01 versus homozygote mutant, by Bonferroni post-hoc tests.