Figure 4.
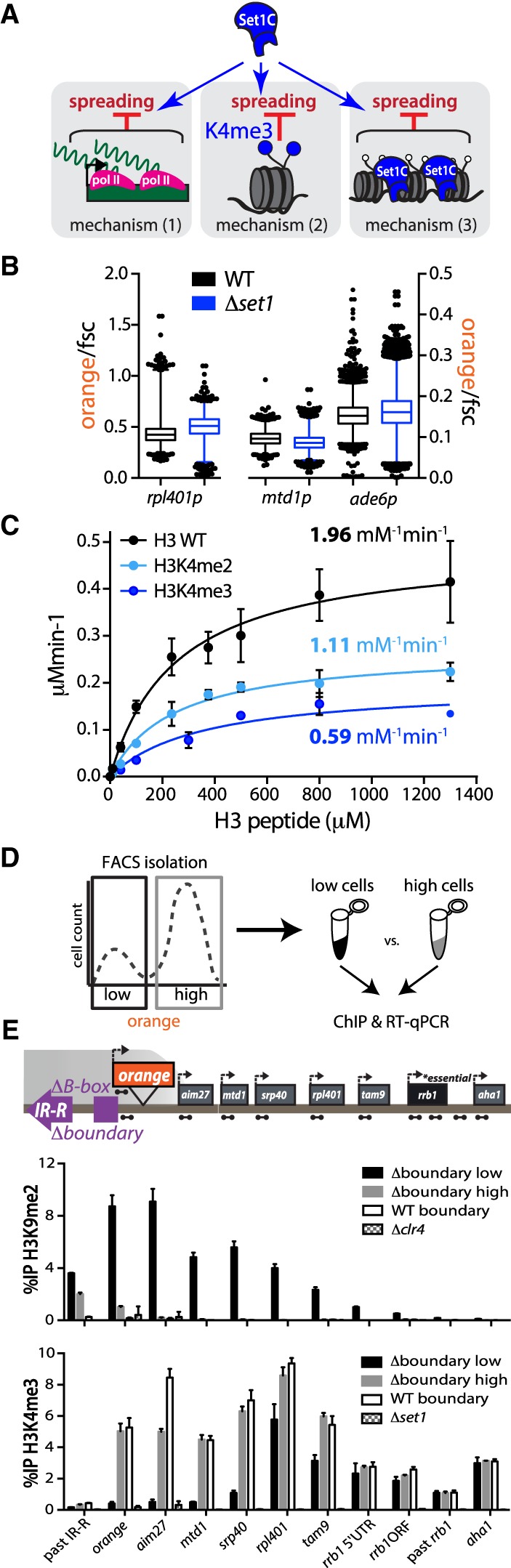
The gene-protective activity of Set1 is independent of mean transcription levels and is rooted in catalytic inhibition of Suv39/Clr4 by H3K4me2/3. (A) Possible mechanisms by which Set1 repels heterochromatin spreading: (1) maintaining a level of transcription that is refractory to heterochromatin invasion due to local RNA polymerase activity and associated cycles of nucleosome eviction; (2) interference of H3K4me3, the Set1 product, with heterochromatin spreading; and (3) noncatalytic effect of Set/COMPASS, including its occupancy on chromatin. (B) Box and whisker plots of “orange” signal normalized to forward scatter (fsc) for rpl401p:HSS, mtd1p:HSS, and ade6p:HSS in set1+ (black) and Δset1 (blue) backgrounds. One percent to 99% of the data are included within the whiskers. Outliers are plotted as individual points. (C) Histone methyltransferase assay with Clr4-SET and H3(1–20) peptides with modifications as indicated. Error bars represent 1SD from three replicate experiments. kcat/KM (specificity constant) values are derived from measurement of the kcat and KM (see Supplemental Fig. S4F). (D) Cartoon overview depicting FACS isolation of “low” and “high” Δboundary 5′ ade6p-“orange” cells followed by ChIP and RT-qPCR. (E) ChIP-qPCR data for FACS-sorted cells: H3K9me2 (top) and H3K4me3 (bottom). Amplicons for each qPCR are depicted as dumbbells on cartoon locus. Error bars represent 1SD from three technical replicate ChIPs.
