Fig. 1. Quantitative assessment for the roles of Trx and GSH systems in control of oxidized sulfur species in vivo.
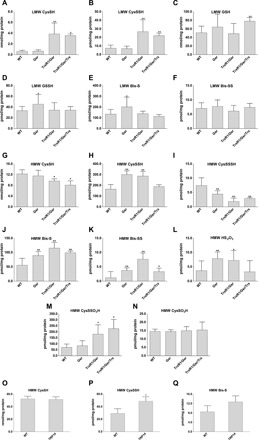
Concentrations of LMW (A to F) and protein-derived (HMW) (G to Q) thiol or persulfide and other oxidized sulfur species were determined using previously described high-sensitivity liquid chromatography–MS/MS protocols with appropriate modifications, as well as a newly developed LC-MS/MS method to detect protein CysSO3H and CysSSO3H (see Materials and Methods). Hepatocytes in the mouse liver tissue samples were WT, homozygous Gsr-null (Gsr), double-homozygous TrxR1/Gsr-null (TrxR1/Gsr), or triple-homozygous TrxR1/Gsr/Trx1-null (TrxR1/Gsr/Trx1). Livers of full-body knockout TRP14-null mice were used in (O) to (Q). The indicated LMW (A to F) and protein-derived (G to Q) sulfur species were extracted from deep-frozen tissue samples as described in Materials and Methods. Analyte levels were normalized to total protein concentrations. Data values and errors are means ± SD of measurements from n = 9 (WT), 8 (Gsr), 7 (TrxR1/Gsr), 5 (TrxR1/Gsr/Trx1), and 3 (TRP14) animals, all gender- and age-matched controls (young female adults) with similar feeding and lightning conditions. Significant differences in values compared to WT are indicated (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).
