Fig. 3. CHK2 phosphorylates FOXK in response to DNA damage in vivo and in vitro.
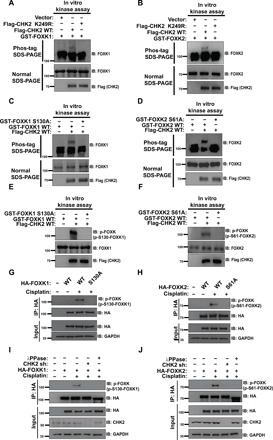
(A and B) Purified Flag-CHK2 WT or Flag-CHK2 K249R proteins from HEK293T were incubated with GST-FOXK1 (A) or GST-FOXK2 (B) in CHK2 kinase buffer at 30°C for 30 min. The samples were separated by Phos-tag SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) gels or normal SDS-PAGE gels as indicated. Phosphorylation was examined using indicated antibodies. (C and D) Purified Flag-CHK2 WT from HEK293T cells was incubated with GST-FOXK1 WT or GST-FOXK1 S130A (C) and GST-FOXK2 WT or GST-FOXK2 S61A (D) in CHK2 kinase buffer at 30°C for 30 min. The samples were separated by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE gels or normal SDS-PAGE gels as indicated. Phosphorylation was examined by probing the blots with the indicated antibodies. (E and F) Samples from (C) to (F) were separated by normal SDS-PAGE gels. Phosphorylation was examined by probing blots with the indicated antibodies (p-FOXK antibody is able to recognize both phosphorylation of FOXK1 at S130 and FOXK2 at S61). (G and H) HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-FOXK1 (G) or HA-FOXK2 (H) and then treated with vehicle or 20 μM cisplatin. HA-FOXK proteins were purified using anti–HA-agarose beads, and proteins bound on Sepharose were blotted with indicated antibodies. (I and J) HA-FOXK1 (I) or HA-FOXK2 (J) were transiently transfected into control cells or CHK2-depleted HEK293T cells. These cells were subsequently treated with vehicle or 20 μM cisplatin for 24 hours. Cells were lysed and purified using anti–HA-agarose beads. One of the samples was additionally treated with λPPase as indicated. The immunoprecipitates were then blotted with the indicated antibodies.
