Figure 9.
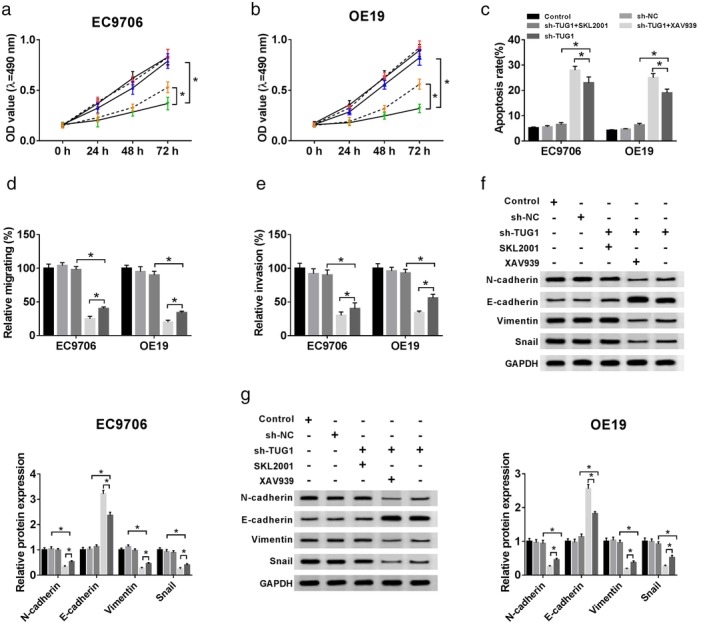
Effects of activating or blocking the Wnt/β‐catenin signaling pathway on cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and migration in EC9706 and OE19 cells after sh‐TUG1 transfection. (a,b) After sh‐TUG1 transfection or combining SKL2001 and XAV939 in EC9706 and OE19 cells, cell proliferation activity was detected by MTT assay, ( ) Control, (
) Control, ( ) sh‐NC, (
) sh‐NC, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, (
) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and (
) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and ( ) sh‐TUG1. (c) the cell apoptosis ability was measured by flow cytometry, (
) sh‐TUG1. (c) the cell apoptosis ability was measured by flow cytometry, ( ) Control, (
) Control, ( ) sh‐NC, (
) sh‐NC, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, (
) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and (
) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and ( ) sh‐TUG1, (d,e) the cell invasive abilities were detected by Transwell assays. (
) sh‐TUG1, (d,e) the cell invasive abilities were detected by Transwell assays. ( ) Control, (
) Control, ( ) sh‐NC, (
) sh‐NC, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, (
) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and (
) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and ( ) sh‐TUG1. (f,g) Western blot assay was carried out to explore the expression of N‐cadherin, E‐cadherin, Vimentin, and Snail in cells. (
) sh‐TUG1. (f,g) Western blot assay was carried out to explore the expression of N‐cadherin, E‐cadherin, Vimentin, and Snail in cells. ( ) Control, (
) Control, ( ) sh‐NC, (
) sh‐NC, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, (
) sh‐TUG1 + SKL2001, ( ) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and (
) sh‐TUG1 + XAV939, and ( ) sh‐TUG1.
) sh‐TUG1.
