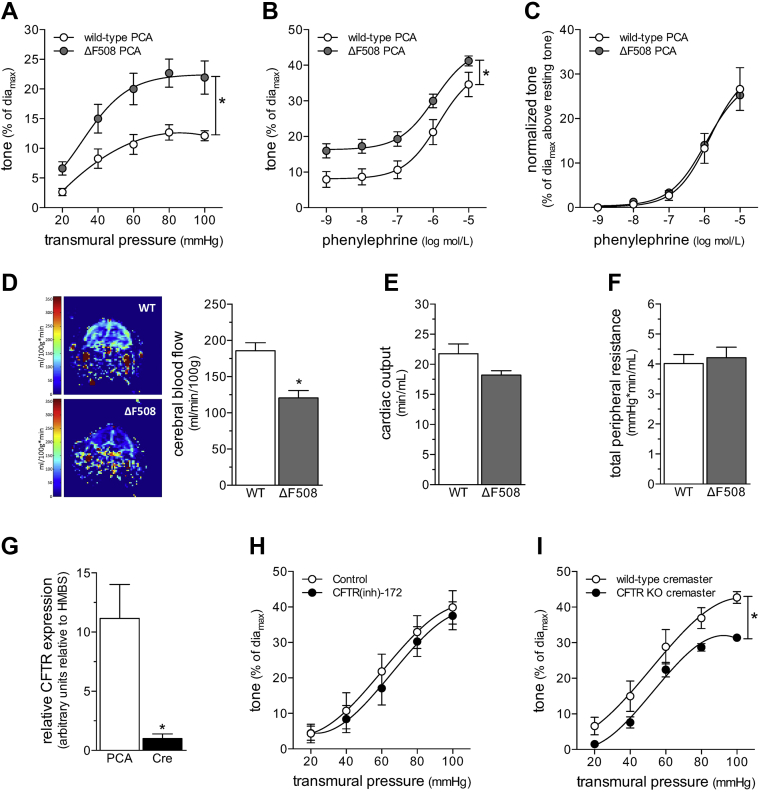
Figure 1.
CBF Is Reduced in CFTRΔF508 Mice
(A) Myogenic vasoconstriction is stronger in posterior cerebral arteries (PCAs) isolated from cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) ΔF508 mutant mice, relative to wild-type (WT) littermate control mice. (B) PCAs isolated from CFTRΔF508 mice display an upward shift in their phenylephrine dose−response relationship. (C) However, once the phenylephrine responses are normalized to basal tone (toneactive − tonerest, where toneactive is the tone at given phenylephrine concentration and tonerest is the tone immediately before stimulation), the WT and CFTRΔF508 phenylephrine dose−response relationships are virtually identical. Mean maximal vessel diameters at 45 mm Hg (diamax) are: CFTRΔF508: 186 ± 2 μm; n = 6 from 4 mice, and WT: 169 ± 8 μm; n = 5 from 3 mice (t-test: p = NS for diamax). (D) Magnetic resonance imaging was used to measure cerebral blood flow in predefined forebrain cortical regions. Representative perfusion maps from WT and CFTRΔF508 mouse forebrains are shown. Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is significantly lower in CFTRΔF508 mice (n = 10), relative to WT littermates (n = 11); however, neither (E) cardiac output (n = 5 for both groups) nor (F) total peripheral resistance (n = 5 for both groups) differed between the 2 genotypes. (G) In WT mice, CFTR mRNA expression is significantly higher in PCAs (n = 5), relative to cremaster skeletal muscle arteries (Cre) (n = 6). (H) Cre myogenic tone is not altered by CFTR inhibition in vitro (100 nmol/l CFTR(inh)-172 for 30 min). (I) However, CFTR gene deletion (CFTR KO) induces a modest, but significant attenuation of myogenic tone. Mean maximal vessel diameters at 60 mm Hg (diamax) are (G) WT: 72 ± 3 μm, n = 5 from 4 mice; (H) CFTR knock out (KO): 88 ± 4 μm, n = 6 from 4 mice; and (H) WT littermates: 78 ± 4 μm, n = 5 from 2 mice. All data are mean ± SEM. In (A to C, H, and I), *p < 0.05 for unpaired comparisons with a 2-way analysis of variance; in (D to G), *p < 0.05 for unpaired comparisons with a t-test.