Figure EV4. Characterization of the RNA‐binding protein QKI in glioblastoma cells.
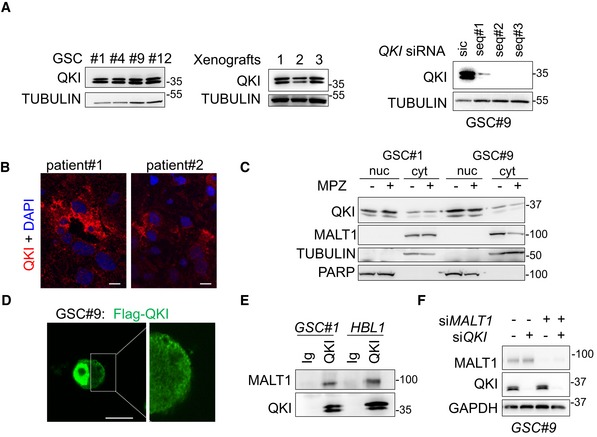
- Western blot analysis of QKI in total protein lysates from GSC #1, #4, #9, #12, and from GSC‐xenografted tumors. Alternatively, GSC#9 were transfected with sic or siQKI using three different duplexes. TUBULIN served as a loading control.
- Confocal analysis of QKI immunostaining (red) in glioblastoma tissue sections from two patients. Nuclei (DAPI) are shown in blue. Scale bars: 10 μm.
- Western blot analysis of QKI in cytosolic (cyt.) and nuclear (nuc.) cell fractionation from GSC#1 and GSC#9, treated with vehicle (−) and mepazine (MPZ, 20 mM, 1 h). TUBULIN and PARP served as loading controls for each fraction. Each panel was replicated at least twice.
- Confocal analysis of FLAG‐QKI (green) localization in transfected GSC#9. Scale bars: 10 μm.
- GSC#1 and HBL1 protein lysates were processed for immunoprecipitation using control immunoglobulins (Ig) and anti‐QKI antibodies. Western blots were performed using anti‐MALT1 and anti‐QKI, as specified.
- GSC#9 were transfected with non‐silencing RNA duplexes (sic), QKI targeting siRNA duplexes (siQKI), MALT1 targeting siRNA duplexes (siMALT1), or double‐transfected with siQKI and siMALT1 and analyzed 72 h later. Knockdown efficiency was checked by Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies.
Source data are available online for this figure.
