Figure 1. Three possible pathogenic mechanisms of non‐coding repeat expansion disorders—example given for C9ORF72 ALS/FTD .
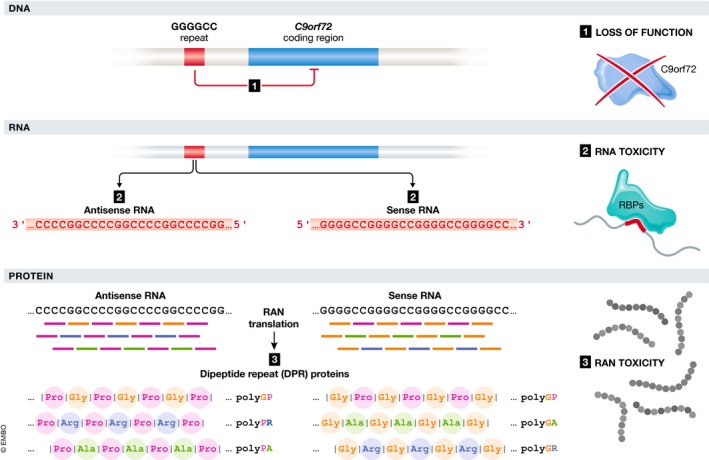
First, the repeat expansion might interfere with the normal transcription of the C9ORF72 gene, leading to loss of function of the C9orf72 protein. Second, repeat‐containing mRNAs might bind to various RNA‐binding proteins, hence disturbing their normal function. This is called “RNA toxicity”. Third, the repeat RNA itself might unconventionally be translated into peculiar toxic RAN peptides. This is called “RAN toxicity”.
