Figure 1. Quantitative FLIM/FRET imaging reveals pleiotropic effects of RanT24N on chromosomal gradients and importin β‐cargo binding.
-
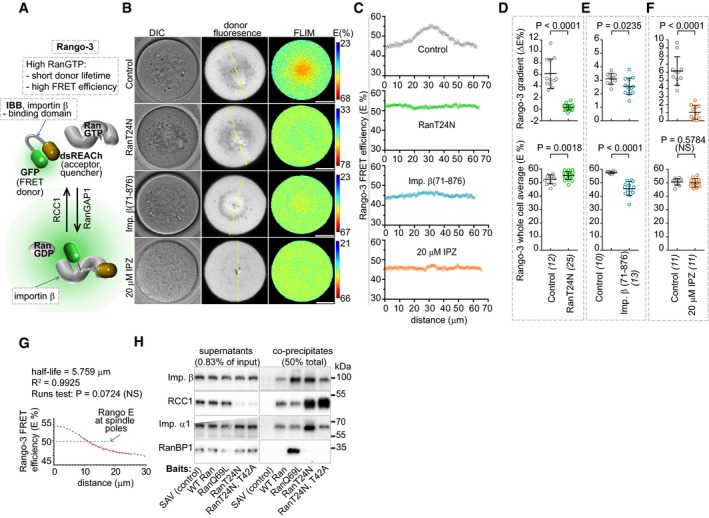
ASchematics of Rango‐3 sensor.
-
BRepresentative images of importin β cargo gradients detected by Rango‐3 FLIM/FRET imaging. Scale bars, 20μm.
-
CLine scans of Rango‐3 FRET efficiency (E) in 10‐μm‐wide areas centered at the dashed lines in (B).
-
D–FQuantification of the Rango‐3 E gradients (top panels) and average cellular Rango‐3 E (bottom) in involving untreated oocytes (controls) or oocytes injected with RanT24N mRNA, importin β(71–876) protein or treated with 20 μM IPZ. Data for each panel are from at least 2 separate experiments. Means ± SDs, t‐test, oocyte numbers indicated in brackets.
-
GNonlinear single‐exponential regression was used to fit the average of radial Rango‐3 τdonor line scans in control oocyte (Fig 1D) with the one‐phase decay model. The dashed line corresponds to the average of spindle pole distance from chromosomes in the same cell.
-
HImmunoblotting in biochemical pulldowns with recombinant Ran proteins added to human DLD1 cell lysates. A representative of at least five repeats.
