Figure 1.
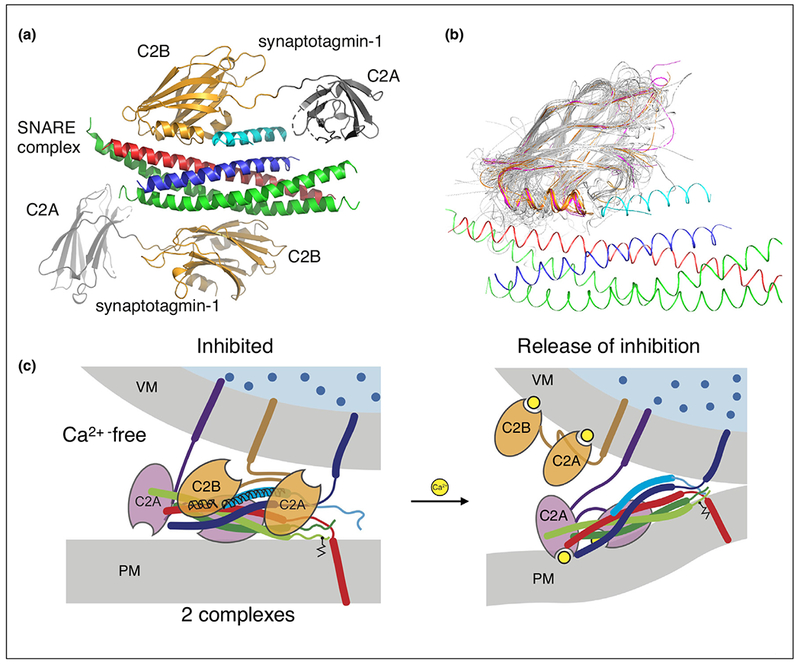
Synaptic fusion complex. (a) Crystal structure of the SNARE/complexin-1/synaptotagmin-1 complex [11••], PDB ID 5W5C (red: syntaxin-1A, green: SNAP-25A, blue: synaptobrevin-2, light blue: central helix of complexin-1, orange: C2B domains of synaptotagmin-1, gray: C2A domains of synaptotagmin-1. (b) Superposition of representative members of the C2 domain superfamily 2.60.40.150 generated by CATH [89] (http://www.cathdb.info) with the structure of the SNARE/complex-1/synaptotagmin-1 complex (red: syntaxin, green: SNAP-25, blue: synaptobrevin, gold: synaptotagmins, purple: Doc2 and Rabphilin, gray: 40 representative structures out of 346 C2 domains with known structure). (c) Release of inhibition model of Ca2+-triggering. Note that it is unknown as to which membrane the Ca2+-bound synaptotagmin-1 C2 domains might interact with. For illustration purposes, we placed it at the synaptic vesicle membrane, although the presence of PIP2 increases the binding affinity between Ca2+-bound synaptotagmin-1 and the membrane, so it also possible, or even likely, that all synaptotagmin-1 C2 domains localize to the plasma membrane upon Ca2+-binding.
